04/19/2024 9:47 a.m.
https://cablematic.com/en/products/vac-surge-protector-220240-sp001p-ac-SJ042/
https://cablematic.com/en/products/vac-surge-protector-220240-sp001p-ac-SJ042/
PVP
€18.73
€5.24
Price including VAT:
€5.24
PVD
€16.46
€4.61
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
Buy before:
Receive it:
Thursday 25
Delivery times are approximate. Cablematic is not responsible for delays.
warranty
returns
OUTLET
Specifications
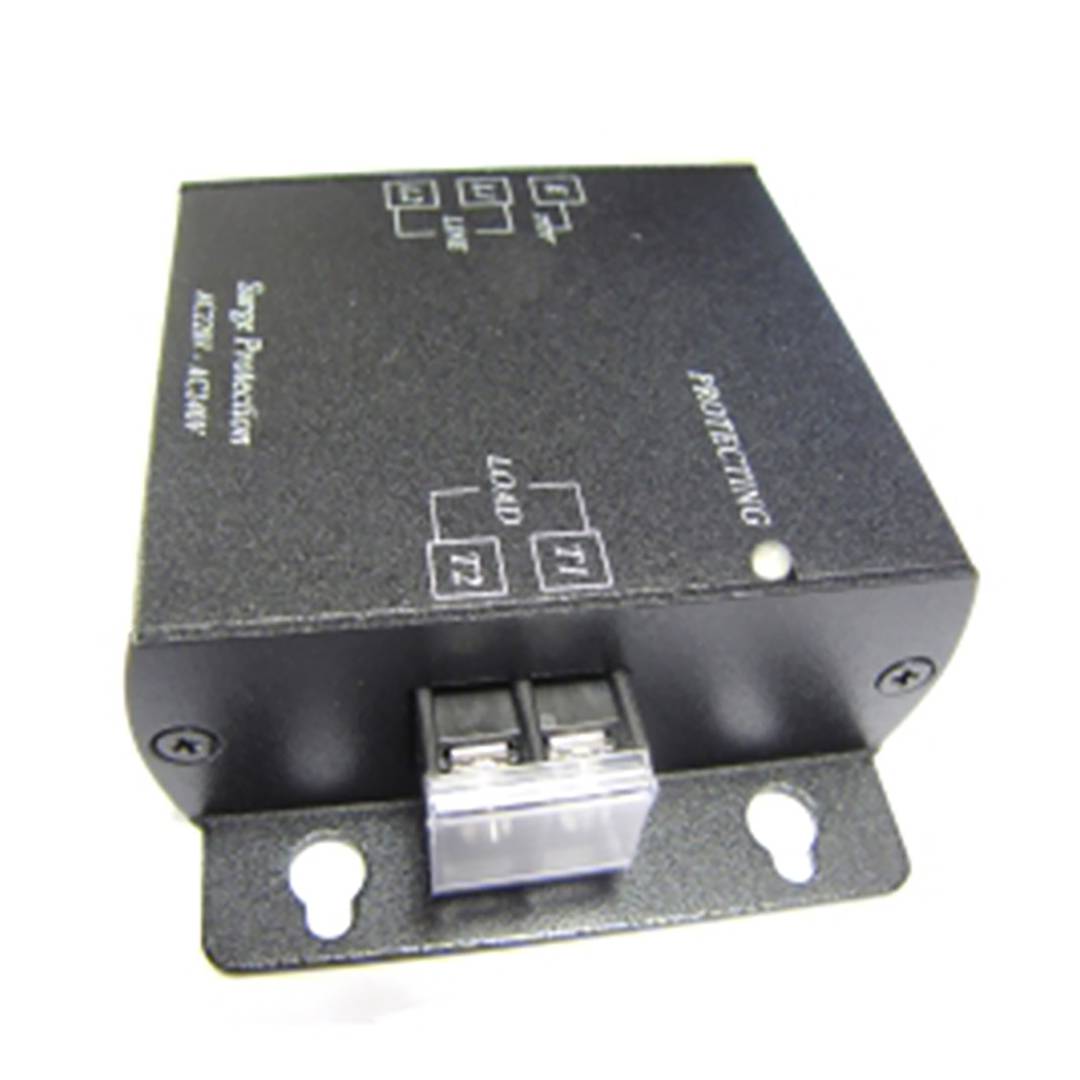
- It is installed between two cables as a splice.
- AC 220-240V protection.
- Maximum withstand voltage protection of 6 KV.
- 300V peak voltage.
- 10A max load.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
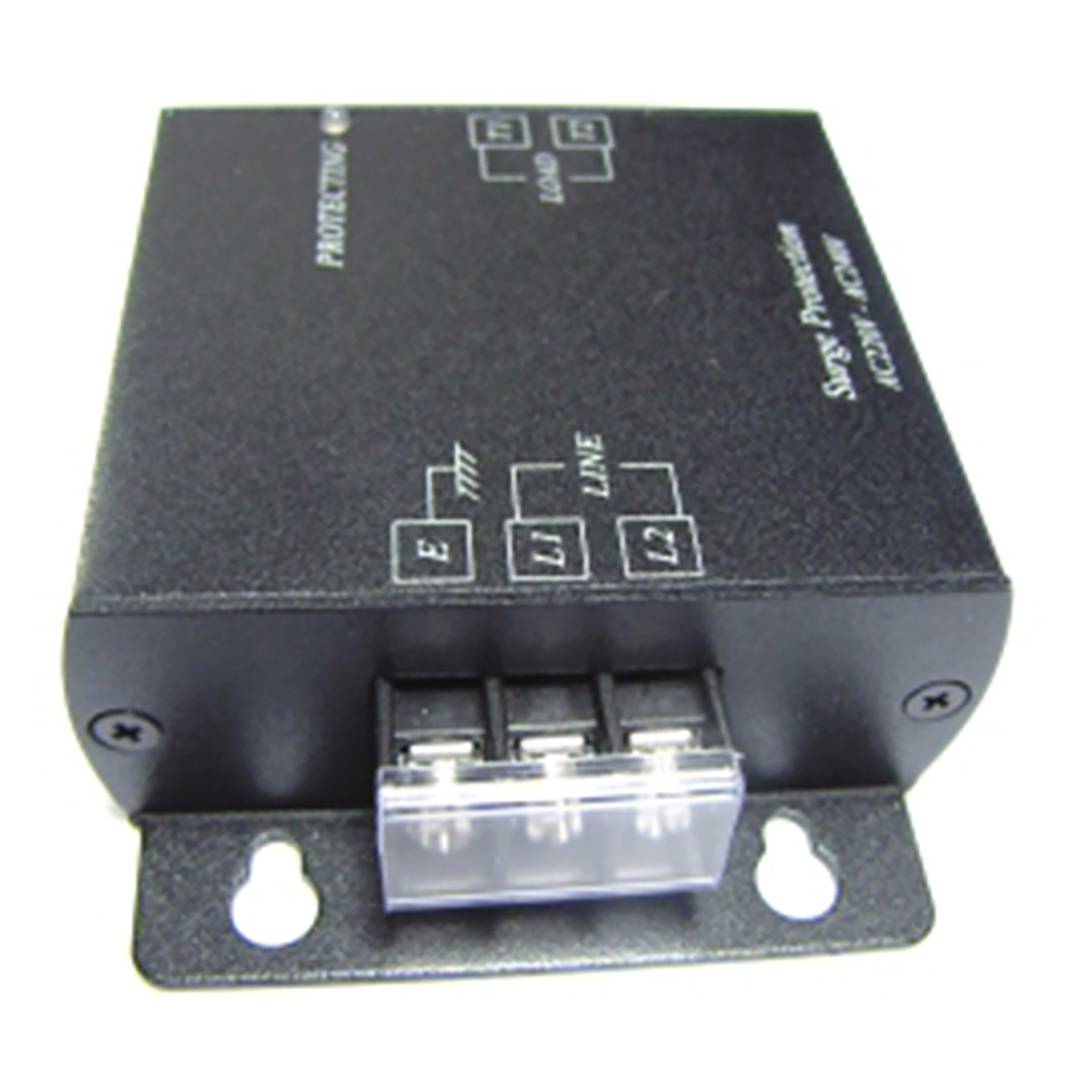
Electrical overload protector is a module with 3 connection terminals on the 220 VAC side (L, N and GND) and 2 terminals on the protected side. It is installed between two cables as a splice, offering a response time of <1 micro second, AC 220-240V protection with a peak voltage > 300 V, maximum withstand voltage protection of 6 KV, maximum load of 10 A and a size of 87 x 67 x 27 mm with a weight of 130 g.
Specifications
Specifications
- It is installed between two cables as a splice.
- AC 220-240V protection.
- Maximum withstand voltage protection of 6 KV.
- 300V peak voltage.
- 10A max load.
- Ideal for protecting electrical devices from electrical surges.
- Gross Weight: 180 g
- Number of packages: 1
Technical terms
- VAC
VAC
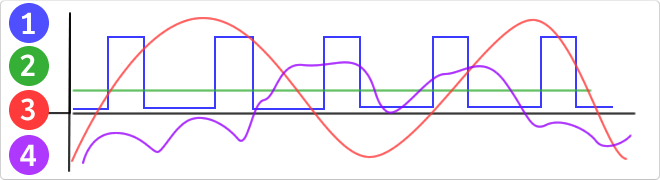
VAC would be the abbreviation of Volt Altern Current which would be translated Volts of alternating current. The difference between VDC is that its sinusoidal oscillation achieving a more efficient energy transmission.
The alternating current is the energy that we receive in our homes, it is generated in the power plants by means of alternators.
The intensity of this type of current varies with time, and changes direction 50 times throughsecond (50hz). The generated voltage changes in the form of sine wave so it is not constant.
In the image:
The alternating current is the energy that we receive in our homes, it is generated in the power plants by means of alternators.
The intensity of this type of current varies with time, and changes direction 50 times throughsecond (50hz). The generated voltage changes in the form of sine wave so it is not constant.
In the image:
- Current by pulsations.
- Direct current (DC).
- Alternating current (AC).
- Variable current.