11/27/2025 3:10 p.m.
https://cablematic.com/en/products/glass-fuse-500ma-5x20mm-10-units-SO070/
https://cablematic.com/en/products/glass-fuse-500ma-5x20mm-10-units-SO070/
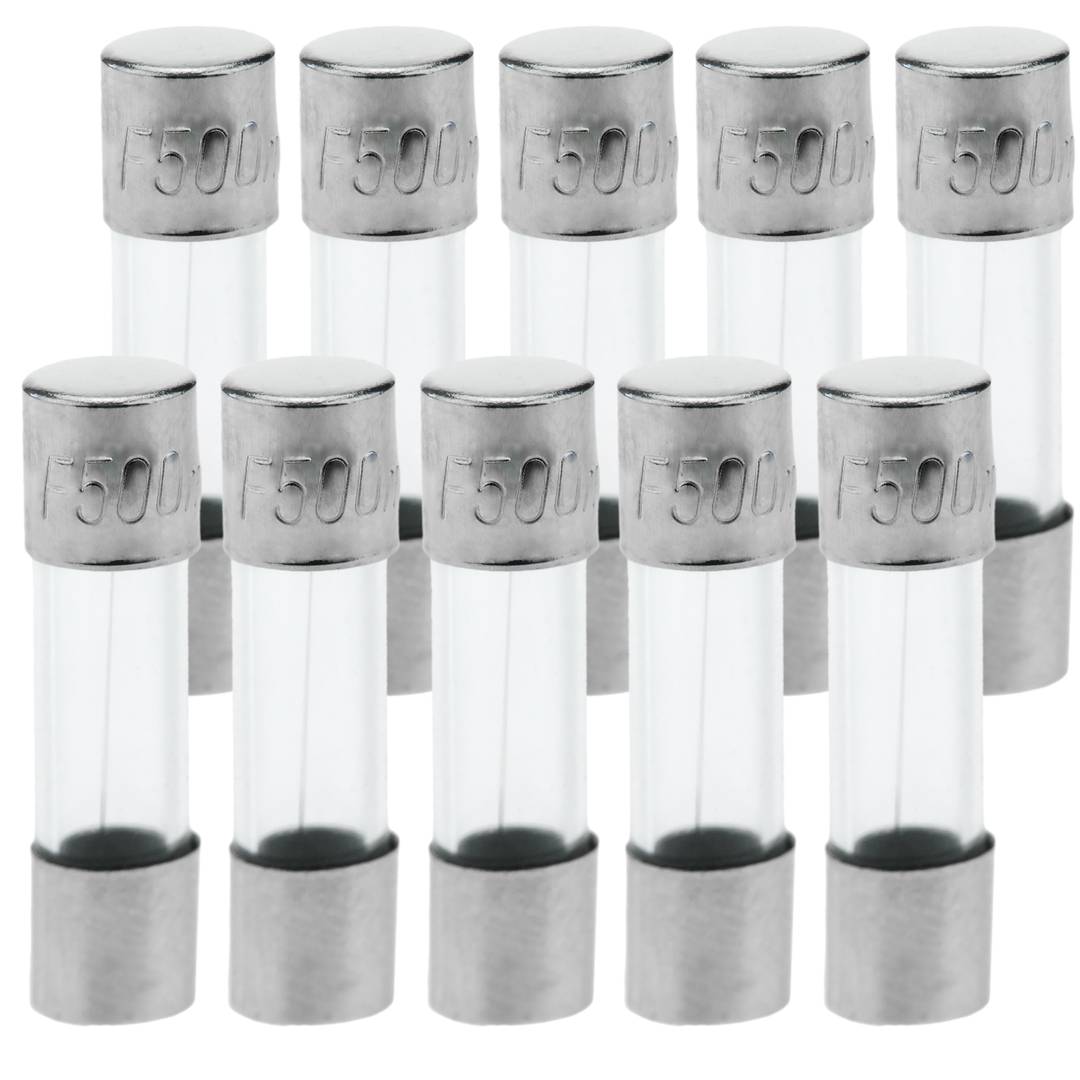
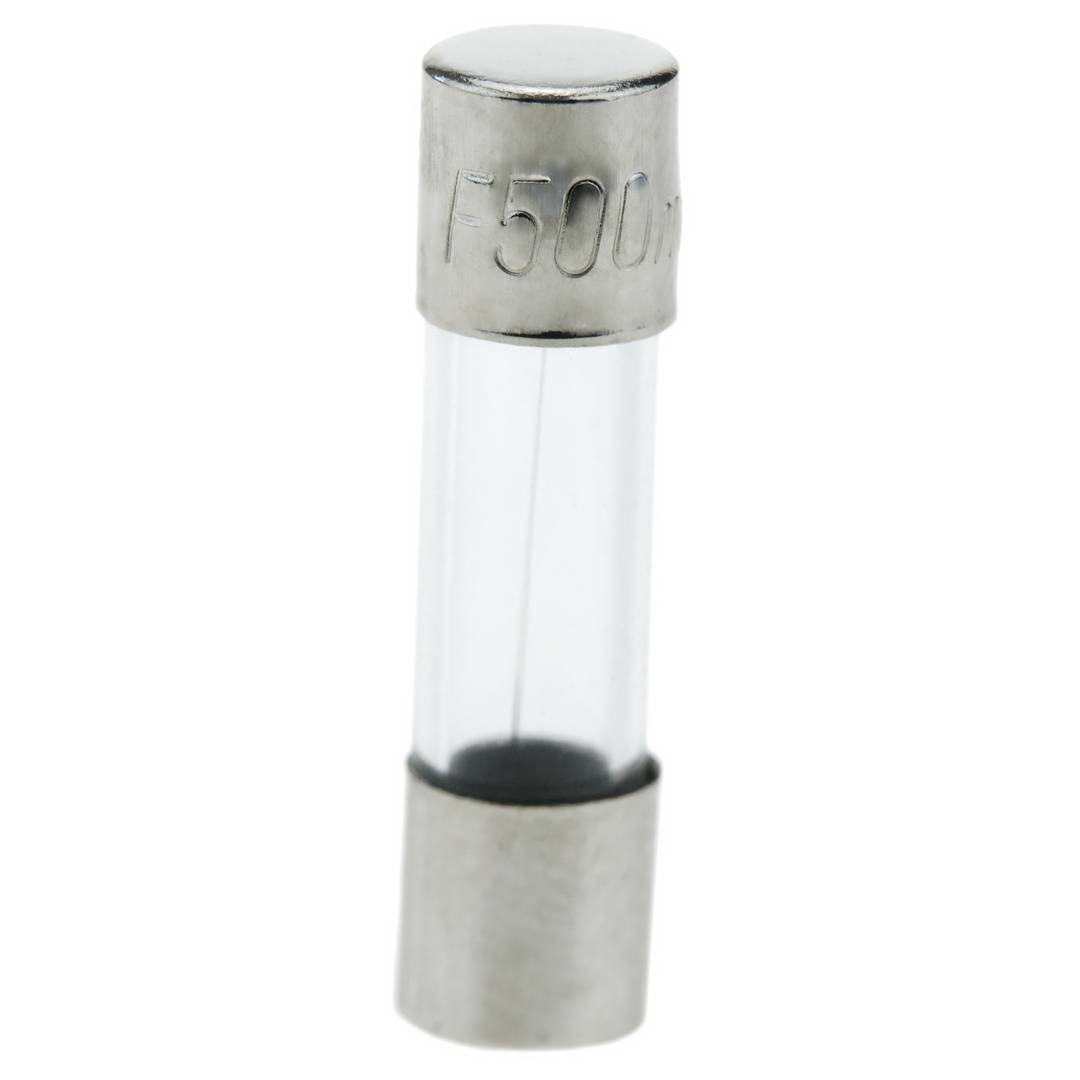
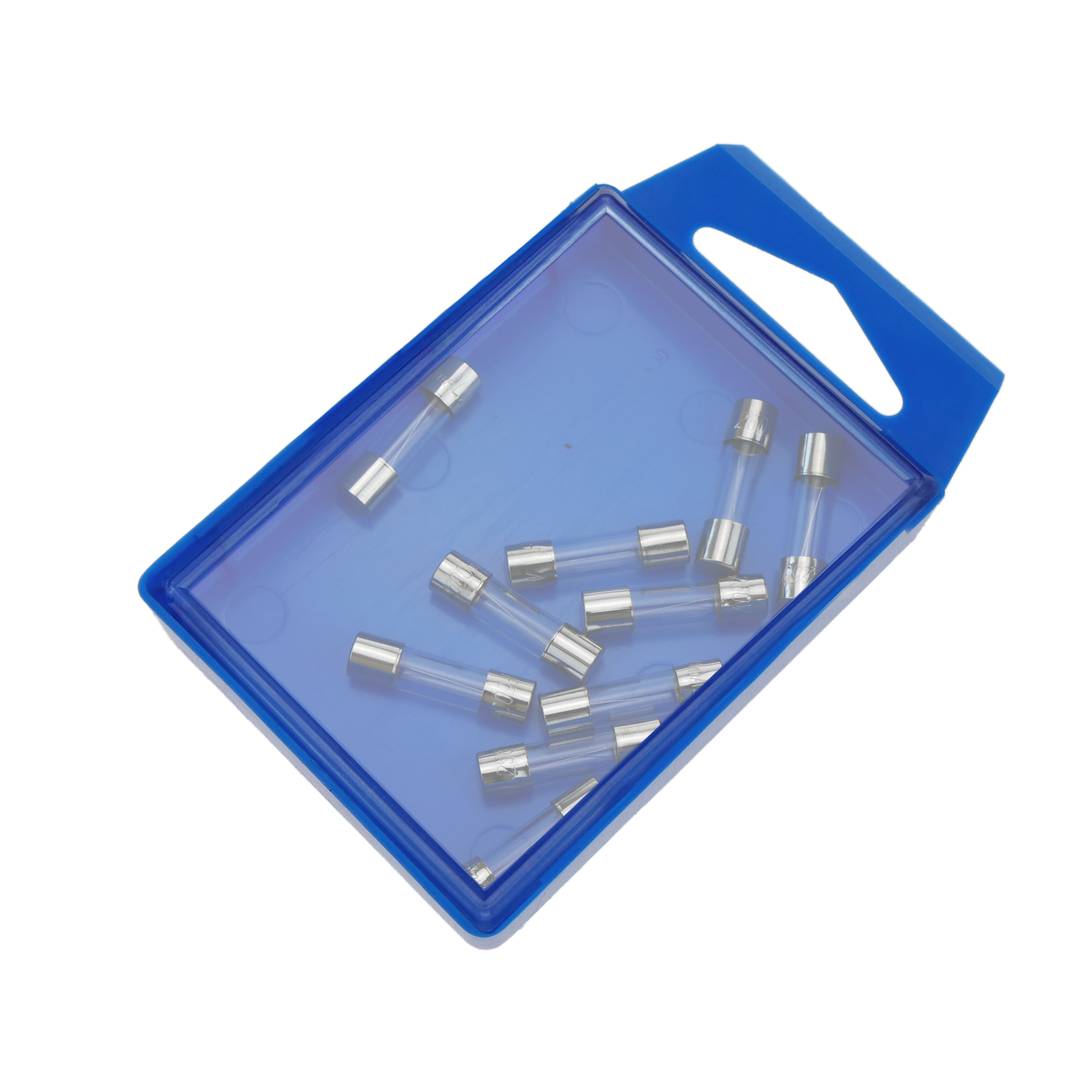
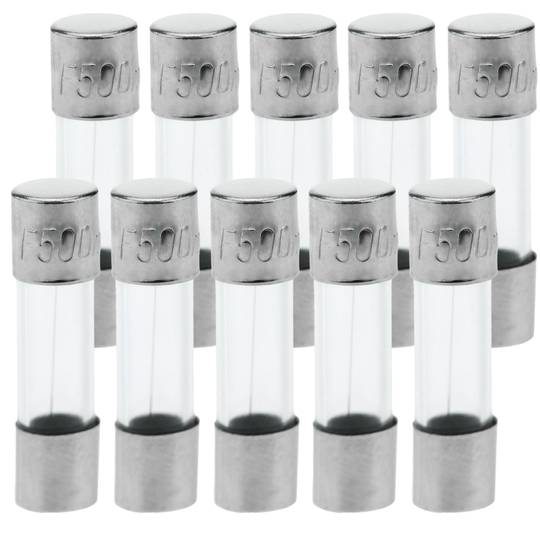
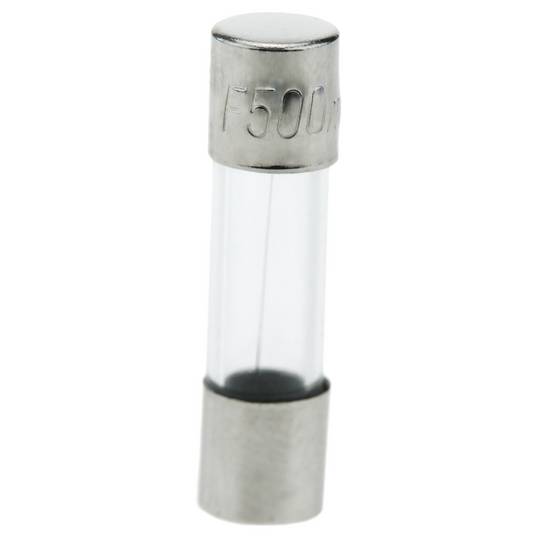
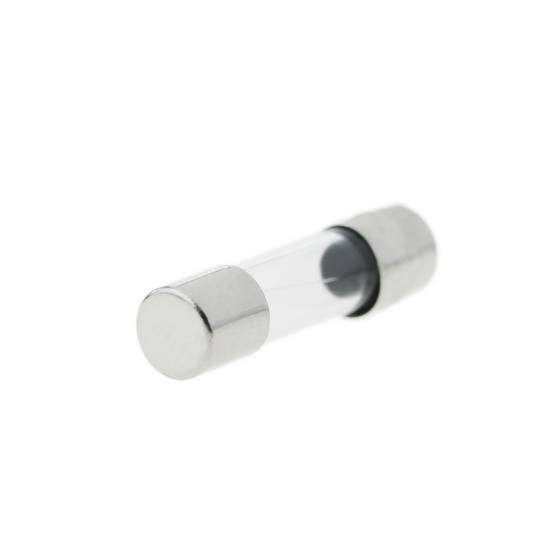
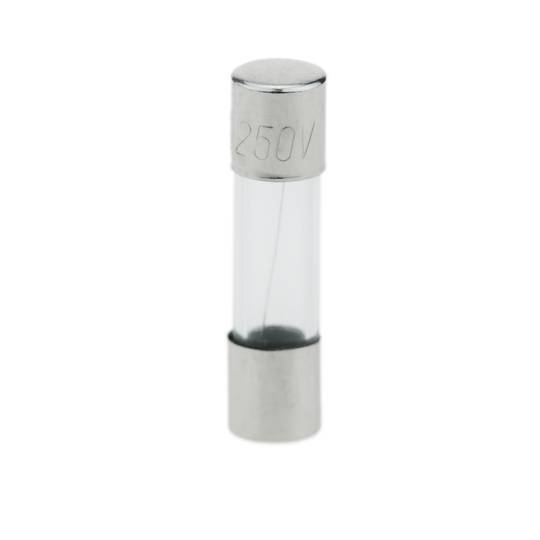
Glass fuse 500mA 5x20mm 10 units
REF: SO070
Specifications
- Glass fuse to protect electrical and electronic devices.
- Rated current of 500mA.
- Size: 5x20mm (5mm diameter and 20mm length).
- Box of 10 units.
- Ideal for automotive electronics, UPS, electric inverters, photo lightsography and any electrical device.
![play_button]() Watch video
Watch video
More info
PVP
€3.12
Price including VAT:
€3.12
PVD
€2.18
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
Immediate delivery
The delivery times are approximate and may vary depending on the selected carrier.
warranty
returns
safe
Specifications
- Glass fuse to protect electrical and electronic devices.
- Rated current of 500mA.
- Size: 5x20mm (5mm diameter and 20mm length).
- Box of 10 units.
- Ideal for automotive electronics, UPS, electric inverters, photo lightsography and any electrical device.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
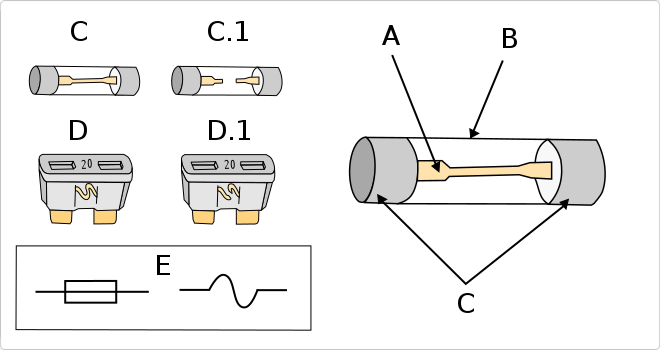
Glass fuse to protect electrical and electronic devices. The fuses allow the passage of the current as long as it does not exceed the maximum amperage value (A) established by each one. If the current is higher than the maximum value, the fuse blows and the circuit is opened so that the current does not pass. This prevents overheating due to excess current and short circuits in all types of devices. Ideal for electronics of automoción, UPS, electric inverters, photography lights and any electrical device.
Specifications
- Glass fuse to protect electrical and electronic devices.
- Rated current of 500mA.
- Size: 5x20mm (5mm diameter and 20mm length).
- Box of 10 units.
- Ideal for automotive electronics, UPS, electric inverters, photo lightsography and any electrical device.
- Gross Weight: 20 g
- Product size (width x depth x height): 2.0 x 0.5 x 0.5 cm
- Number of packages: 1
- Packages size: 8.8 x 5.2 x 1.5 cm
Technical terms
- UPS
- Types of fuses
UPS
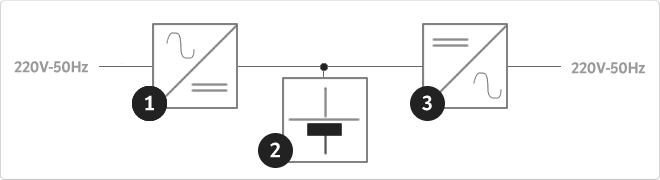
An uninterruptible power supply, UPS, also known as UPS (uninterruptible power supply English), is a device that, thanks to batteries or other energy storage elements, can provide power for a limited time and for a blackout all the devices connected. Other features that can be added to these teams is to improve the power qualityéctrica reaching loads, ups and downs filtering and eliminating voltage harmonics of the network in the case of using AC. There are different types of UPS UPS DC loads connected to the UPS require DC power, so they will transform the alternating current to direct current sales network and use it to power the load and store it in your batterys. So they do not require converters between the batteries and loads. UPS AC UPS obtained These outputs an AC signal, so they need an inverter to convert the direct signal from the batteries in an alternating signal. UPS standby (Standby Power Systems) This system has two main circuits: the power line, which only addsa stabilized and additional filtering of each team to normal feed, and the actual circuit UPS circuit whose core is called "inverter". It is called system "standby" or waiting, because the circuit of alternative power, the inverter is "offline" or inactive, waiting to become operational when it produces a failure in the power supply. It has a switching element that connectsand either circuit switched alternately. UPS line-interactive (in-line) This type of UPS regulates voltage variations by elevations or reductions in mains voltage. During these interventions, the UPS uses its battery to perform the voltage regulation. UPS online (online) In contrast, the UPS "online" (on-line), the battery and the inverter are permanently It is utiized, ensuring a maximum response in a timely manner before the event of network failure. In addition, they can also correct the frequency shifts as re-generate the ac wave permanently. Diagram UPS online In the picture (1) Rectifier The picture (2): battery in the picture (3): Inverter