12/24/2025 12:47 p.m.
https://cablematic.com/en/products/riser-card-6660mm-1-agp-CR062/
https://cablematic.com/en/products/riser-card-6660mm-1-agp-CR062/
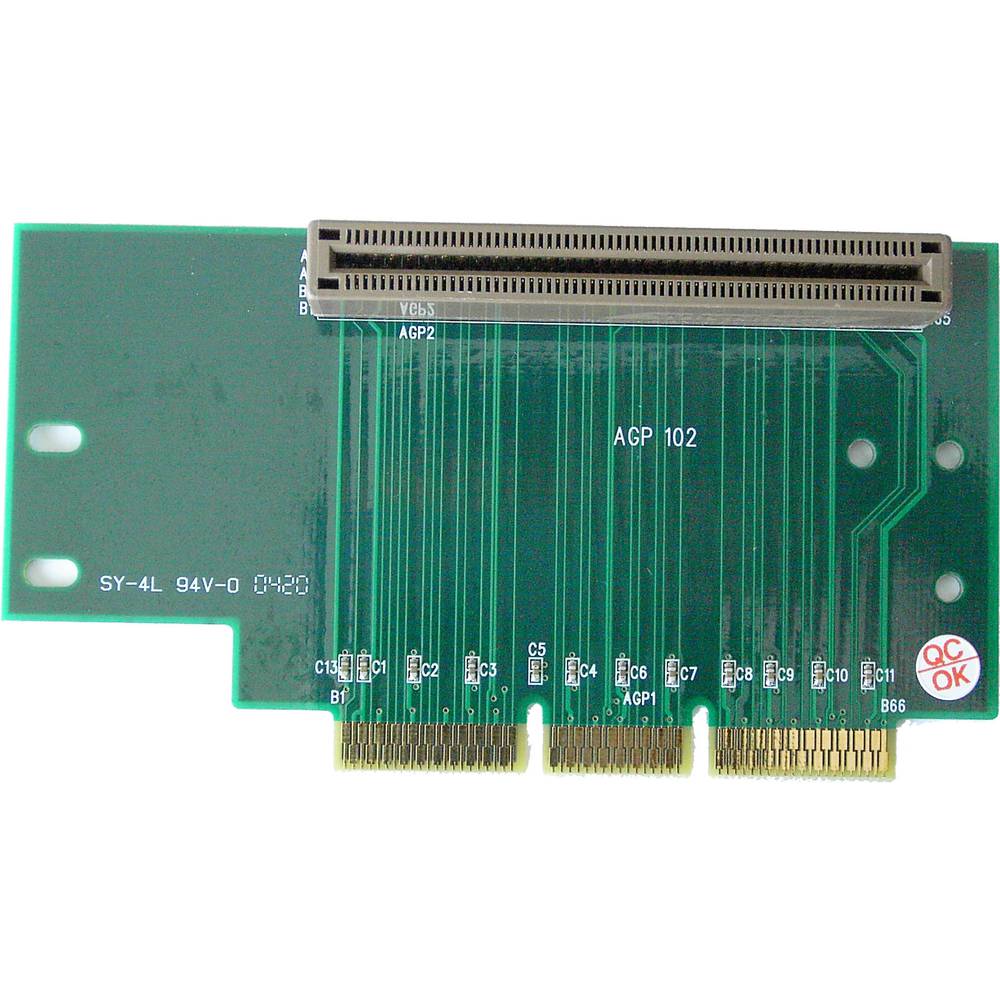
Riser Card 66.60mm (1 AGP)
REF: CR062
Specifications
- Riser Card size 121 x 66.6 x 1.6 mm and a 132-pin AGP slot (8X, 4X and 2X) in horizontal arrangement.
- 4-layer plate design.
- Protection against electric shock.
PVP
€1.30
Price including VAT:
€1.30
PVD
€1.14
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
Immediate delivery
The delivery times are approximate and may vary depending on the selected carrier.
warranty
returns
safe
Specifications
- Riser Card size 121 x 66.6 x 1.6 mm and a 132-pin AGP slot (8X, 4X and 2X) in horizontal arrangement.
- 4-layer plate design.
- Protection against electric shock.
More info
Riser Card size 121 x 66.6 x 1.6 mm and a 132-pin AGP slot (8X, 4X and 2X) in horizontal arrangement. 4-layer plate design. Protection against electric shock.
- Gross Weight: 50 g
- Number of packages: 1
Technical terms
- riser card
riser card
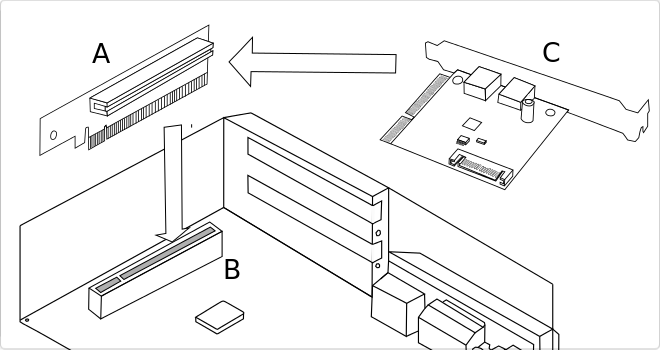
Riser Card (A) is the name given to the board that contains the printed circuit, which through signal connectors is capable of transmitting data and power using a single connector.
This type of connector is compatible with motherboards or expansion slots (B), which is responsible for managing and distributing the signals, although we can also find that this communication is carried out by cable, using flex connection hoses.
The main function of a riser card is to be able to adapt an expansion card (C) in a system in which it is possible due to size or distribution, normally creating an angle of 90° between the plate and the card.
For example, a riser card could be used in a low profile PC to accommodate a larger size card or a 1U PC case could be fitted to accommodate larger cards.
This type of connector is compatible with motherboards or expansion slots (B), which is responsible for managing and distributing the signals, although we can also find that this communication is carried out by cable, using flex connection hoses.
The main function of a riser card is to be able to adapt an expansion card (C) in a system in which it is possible due to size or distribution, normally creating an angle of 90° between the plate and the card.
For example, a riser card could be used in a low profile PC to accommodate a larger size card or a 1U PC case could be fitted to accommodate larger cards.