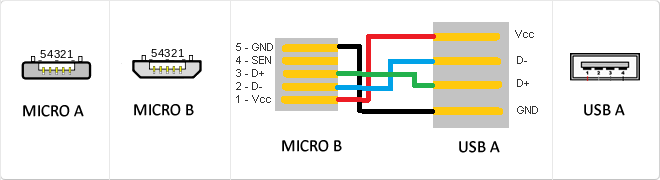
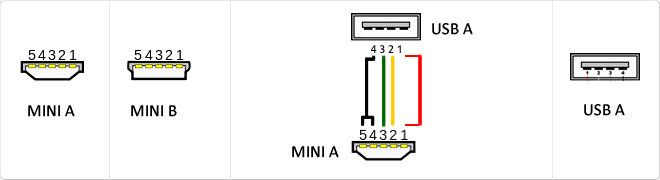
MicroUSB
or horizontal. The micro USB with five pins, which pins identification (ID) Micro AB USB connectors special work. AB connectors with pin ID can allow the device to function as a connector A or B to standard USB technology. This gives the new smart phones and other devices the option to act as either a single storage device or as provi
USB
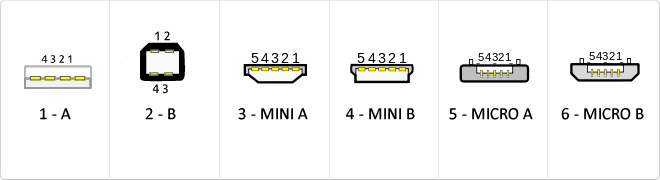
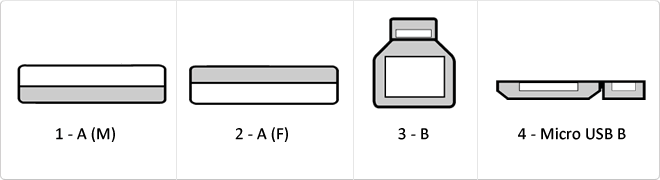
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard that defines the cables, connectors and used a bus to connect, communicate, computers, peripherals and electronic devices protocols Transmission Rates Low speed (USB 1.0). Transfer rate up to 1.5 Mbit/s (188 kB/s) used in keyboard, mouse ... transfer rate up to 12 Mbit/s (1.5 MB/s) High Speed ??(USB 2.0): Rate transferencia up to 480 Mbit/s (60 MB/s) SuperSpeed ??(USB 3.0) transfer rate up to 4.8 Gbit/s (600 MB/s) Connector Types 1 - USB type A (4 pin) 2. - USB type B (4 pin) 3 - Mini A (5-pin) 4 - Mini B (5-pin) 5 - Micro A (5-pin) 6 - Micro B (5-pin)
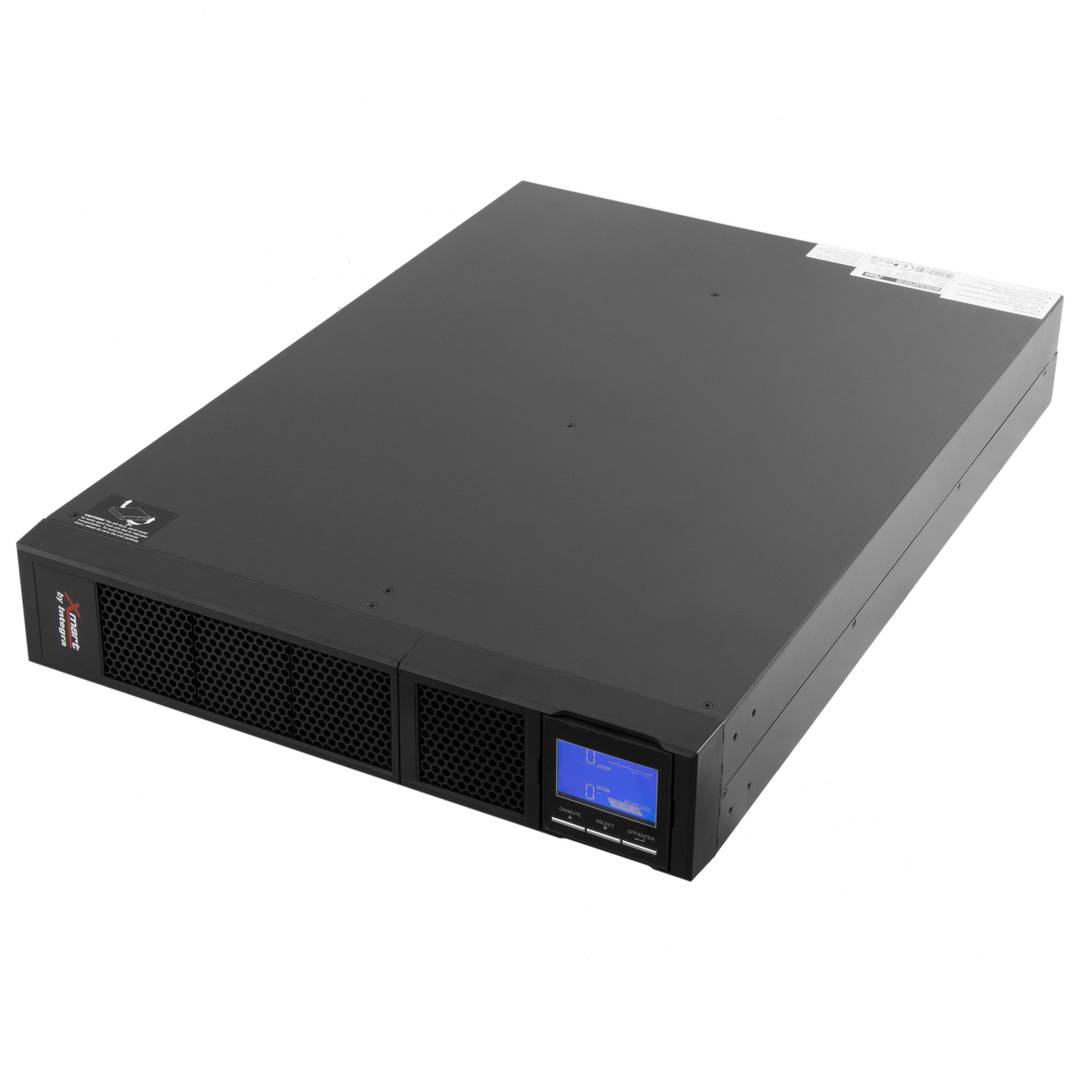
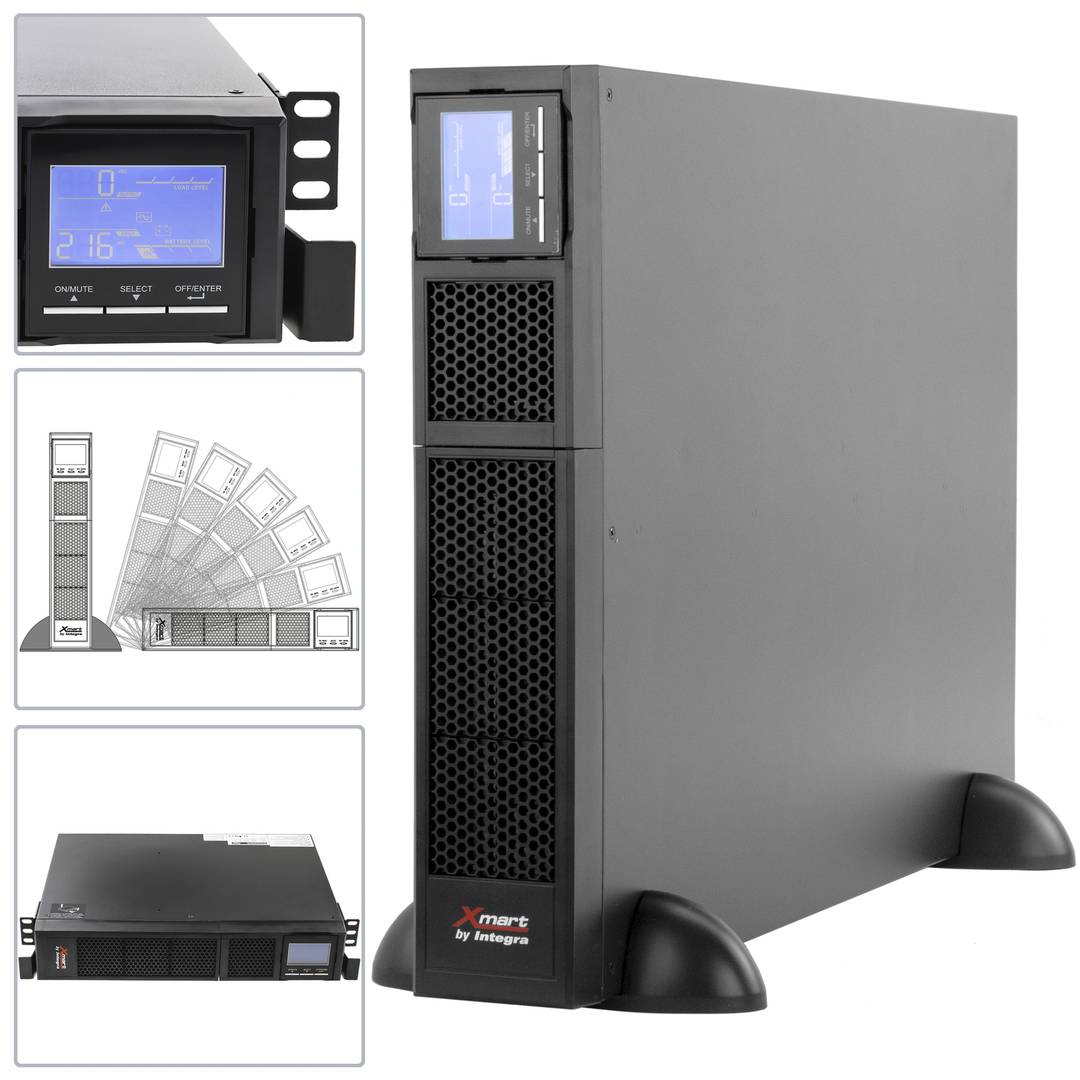
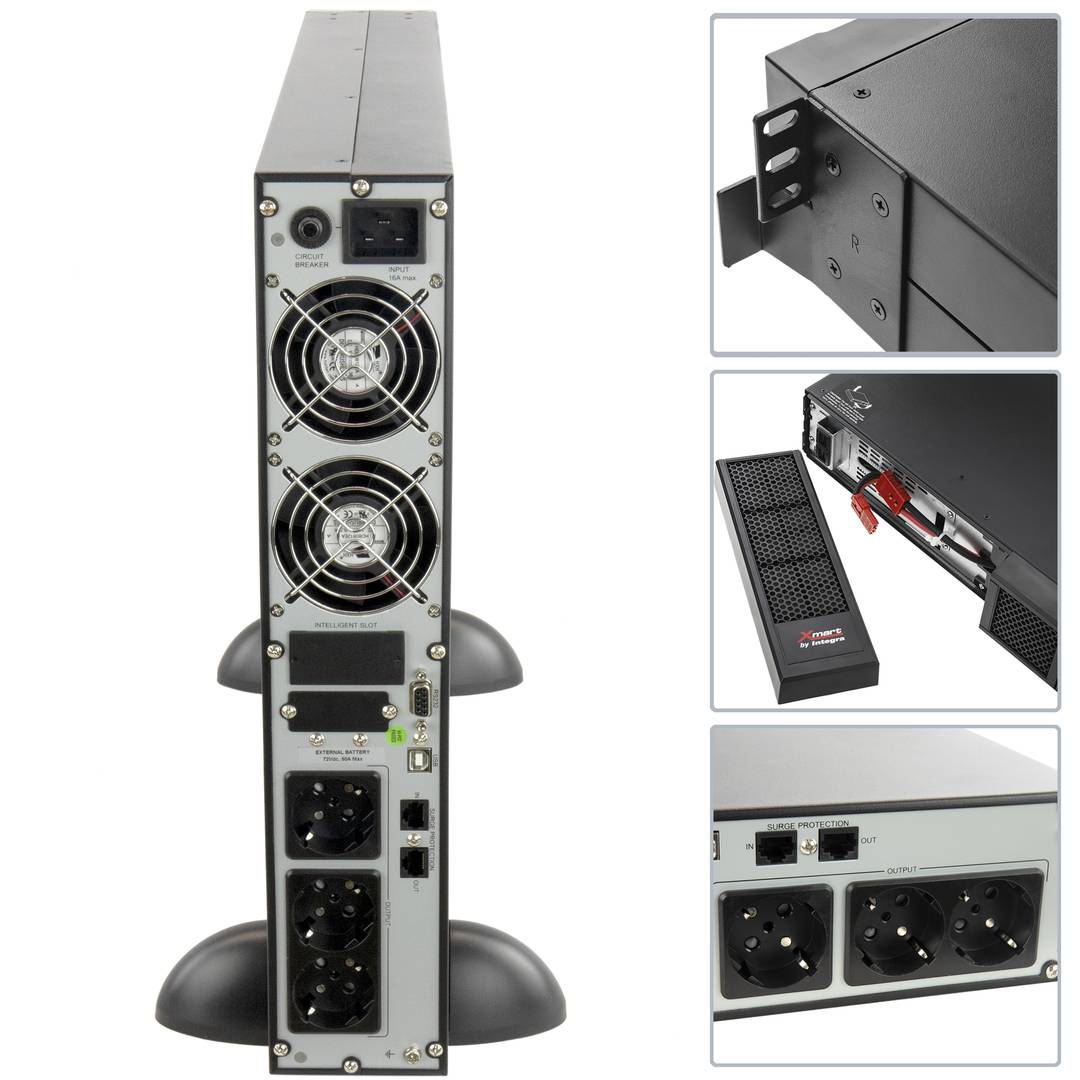
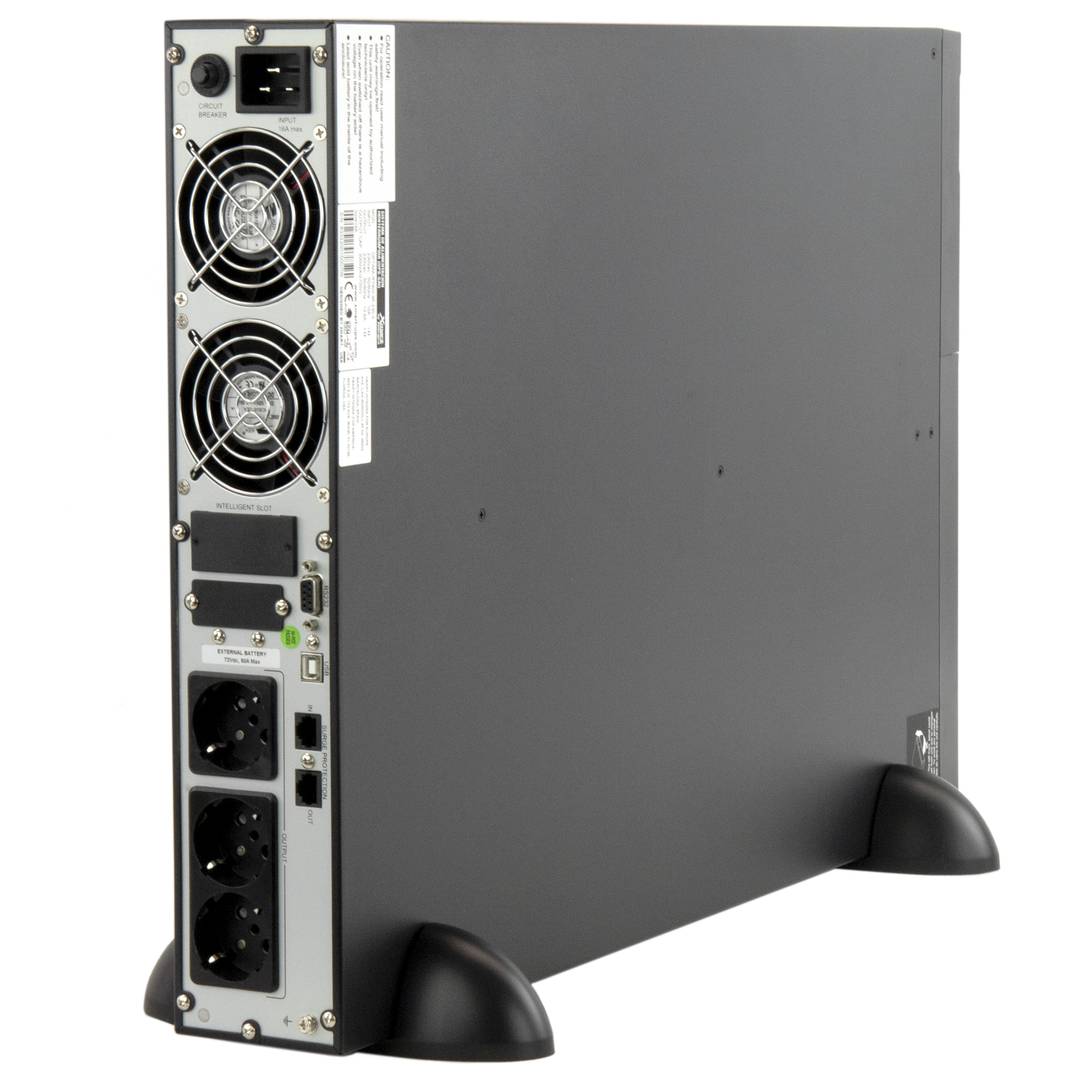
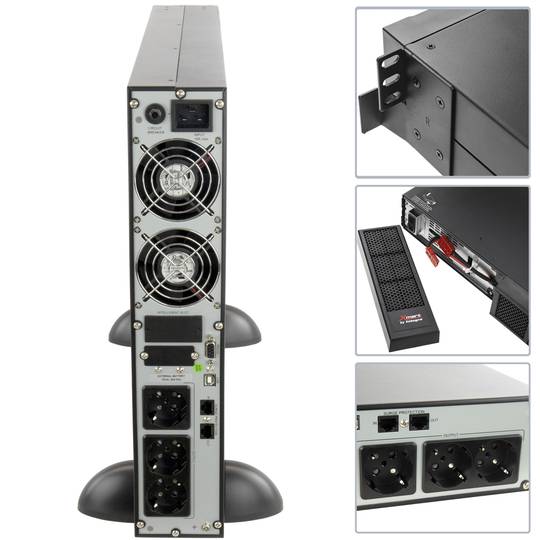
UPS
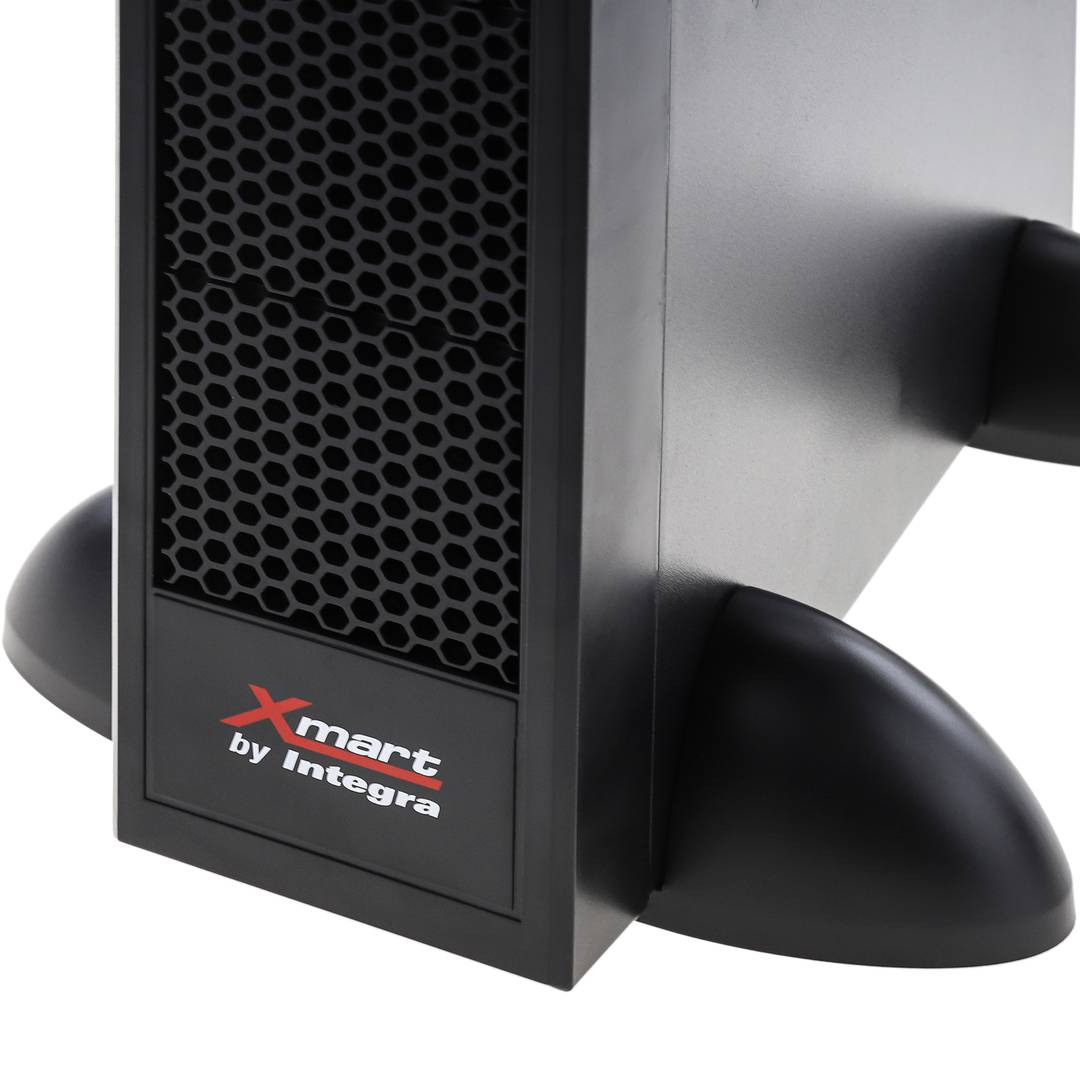
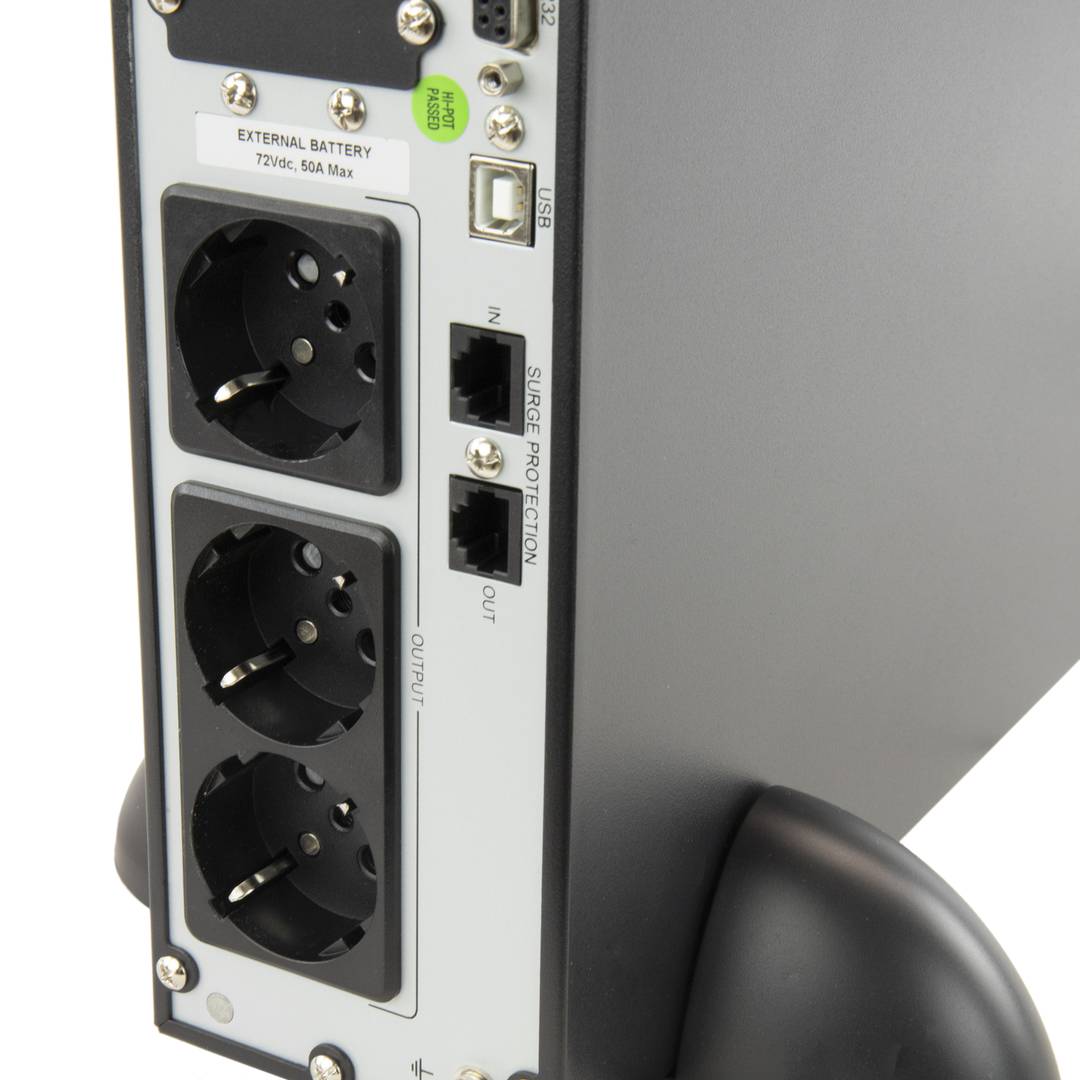
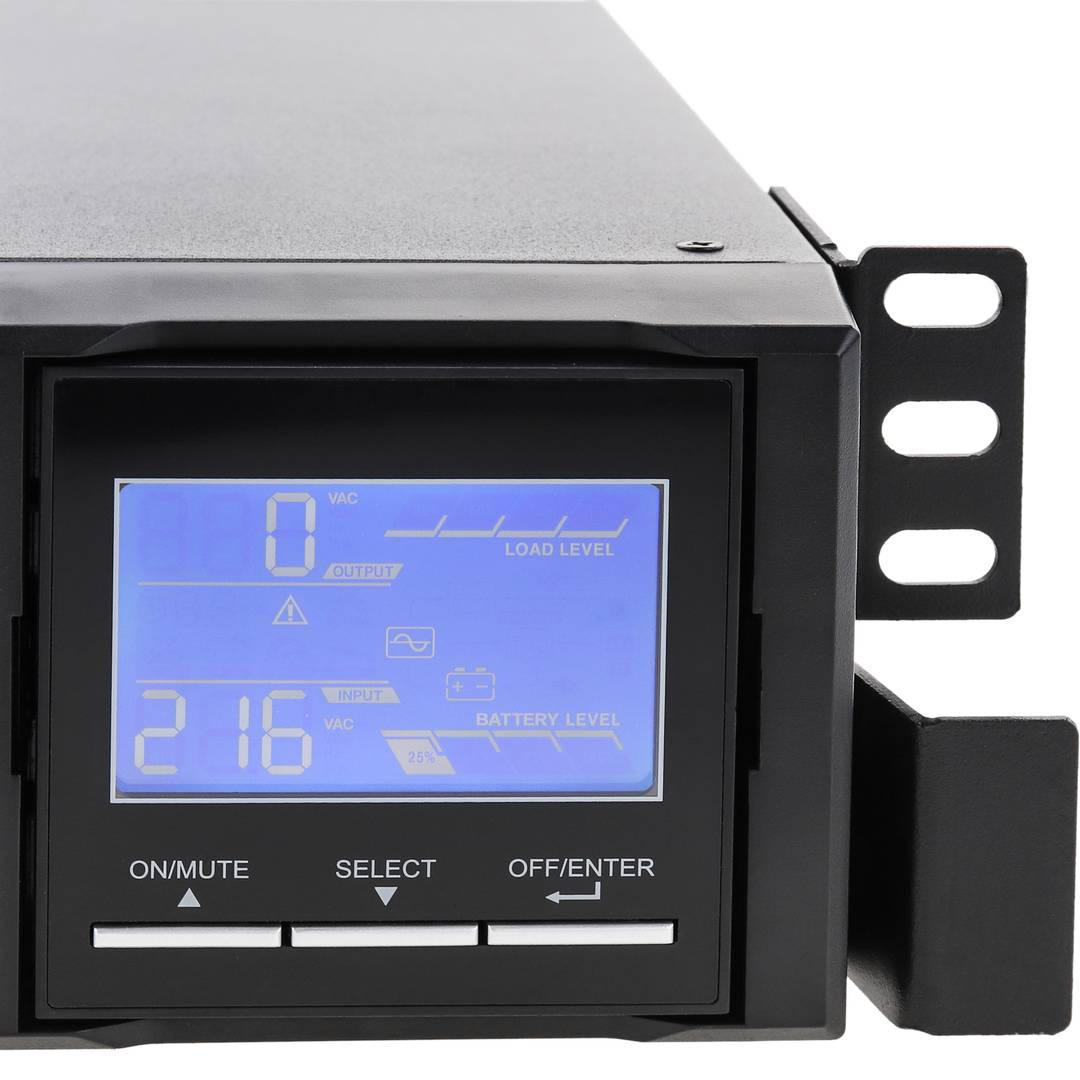
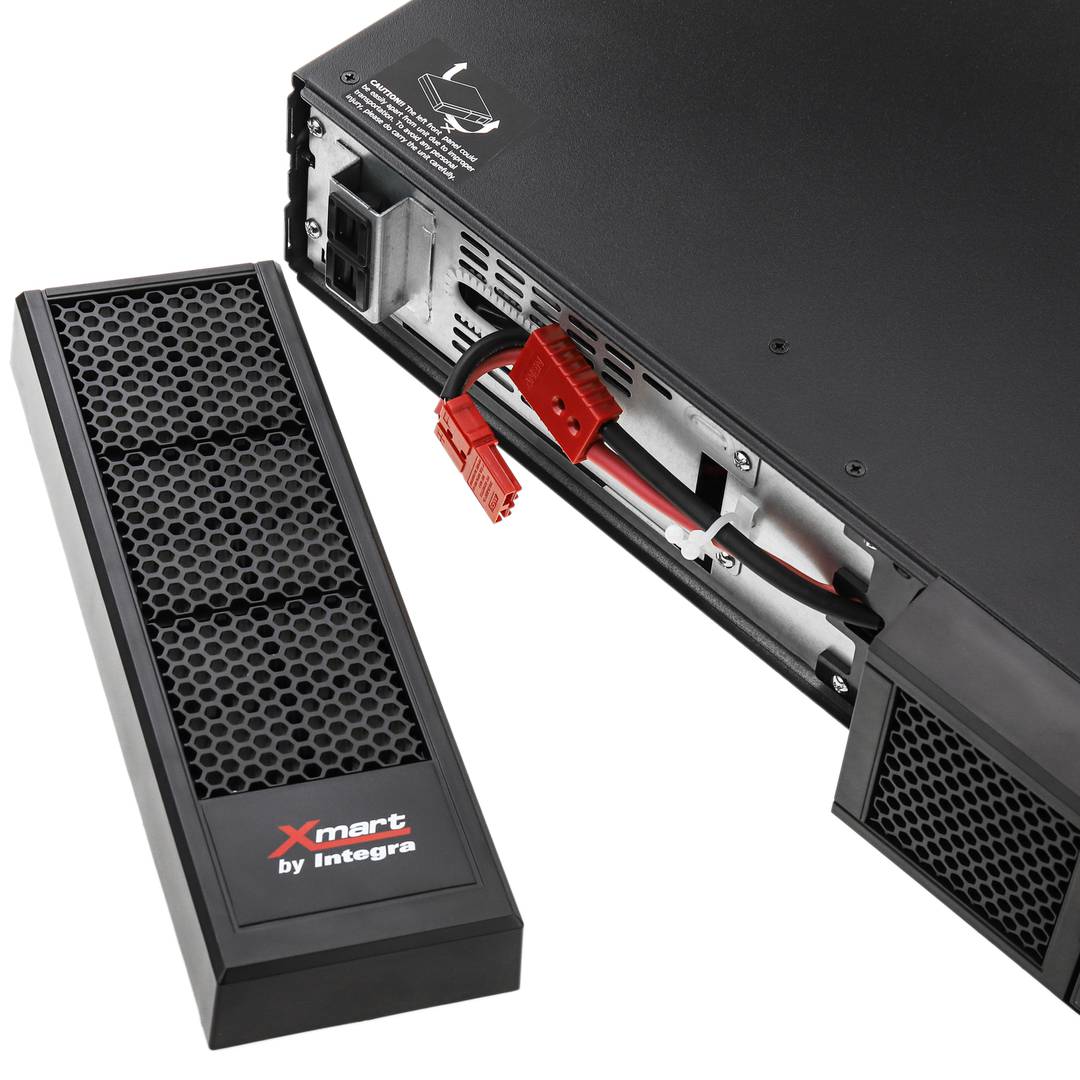
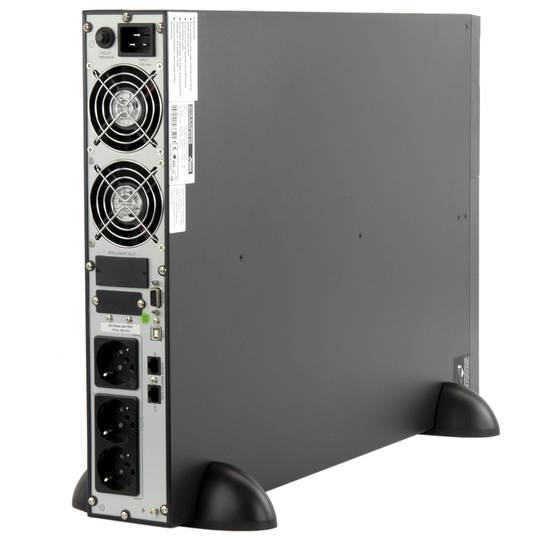
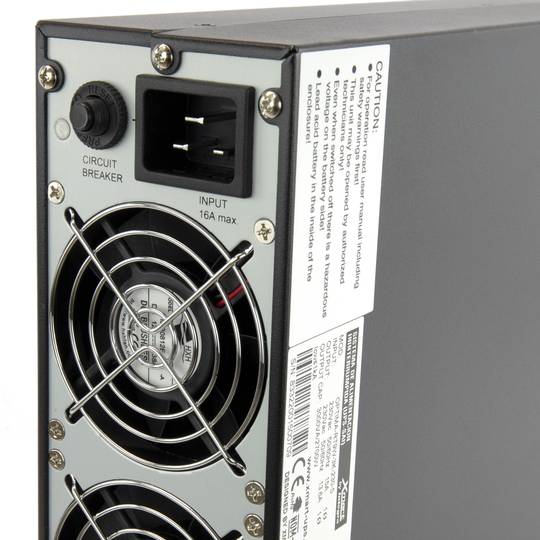
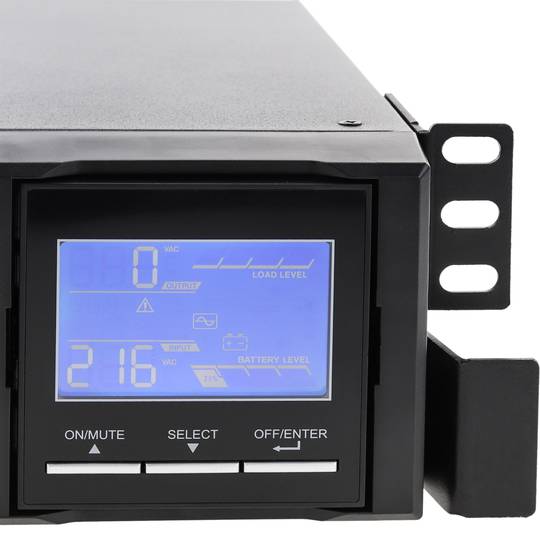
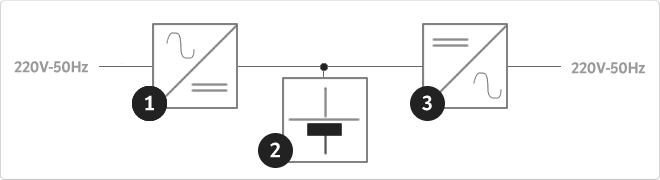
An uninterruptible power supply, UPS, also known as UPS (uninterruptible power supply English), is a device that, thanks to batteries or other energy storage elements, can provide power for a limited time and for a blackout all the devices connected. Other features that can be added to these teams is to improve the power qualityéctrica reaching loads, ups and downs filtering and eliminating voltage harmonics of the network in the case of using AC. There are different types of UPS UPS DC loads connected to the UPS require DC power, so they will transform the alternating current to direct current sales network and use it to power the load and store it in your batterys. So they do not require converters between the batteries and loads. UPS AC UPS obtained These outputs an AC signal, so they need an inverter to convert the direct signal from the batteries in an alternating signal. UPS standby (Standby Power Systems) This system has two main circuits: the power line, which only addsa stabilized and additional filtering of each team to normal feed, and the actual circuit UPS circuit whose core is called "inverter". It is called system "standby" or waiting, because the circuit of alternative power, the inverter is "offline" or inactive, waiting to become operational when it produces a failure in the power supply. It has a switching element that connectsand either circuit switched alternately. UPS line-interactive (in-line) This type of UPS regulates voltage variations by elevations or reductions in mains voltage. During these interventions, the UPS uses its battery to perform the voltage regulation. UPS online (online) In contrast, the UPS "online" (on-line), the battery and the inverter are permanently It is utiized, ensuring a maximum response in a timely manner before the event of network failure. In addition, they can also correct the frequency shifts as re-generate the ac wave permanently. Diagram UPS online In the picture (1) Rectifier The picture (2): battery in the picture (3): Inverter
![]()
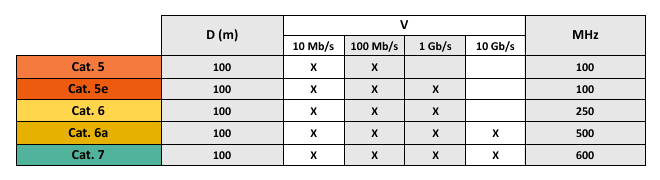
Categories network cables
Depending on the quality and type, network cables are classified into categories that help us know the characteristics of them.
The categories of network cables most commonly used are:
- Category 5
- Category 5e
- Category 6
- Category 6
- Category 7
As can be seen, category 5e (enhanced or improved) and category 6A (Augmented), are an improvement of categories 5and 6, respectively, which it has improved the top speed and bandwidth.
The higher the category, the higher the speed of maximum data, the maximum 100 meters distance as its standard.
You can see a table which shows the 5 categories, where V is the maximum velocity, D is the maximum and MHz frequency which can work away.
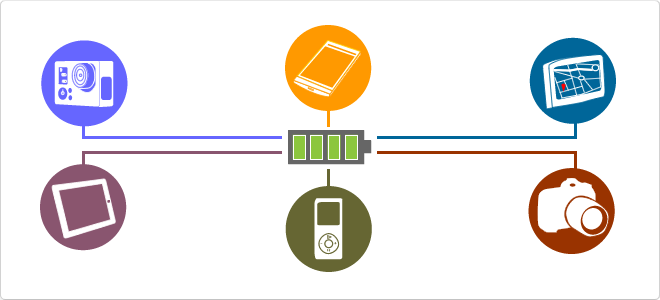
Power Bank
The battery bank or Power Bank is an ideal solution if you are running out of battery on your device when you really need it.
It's charged using a miniUSB or microUSB cable directly connected to a power source or USB port (PC or MAC).
Its operation is very simple, you only need to connect the battery bank to your smartphone, tablet, MP3, Ipod, etc. and automatically will start charging.
The provided charge to the device depends on the capacity in mAh of the battery bank, usually can perform a full charge of a device and depending on the capacity of the power bank, it can do it a few times.
To calculate the times you can charge your device simply divide the capacity of powerbank between the battery capacity of the device.
Example:
If the battery bank is 7.200mAh i your device is an Apple iPhone, Samsung Galaxy or similar with 1.800mA battery, you can charge up to 4 times without going through the plug.
The charging time of your device using a powerbank is very similar to the charging time using the original charger.
Ideal for long trips, meetings, campsites, etc.
![]()
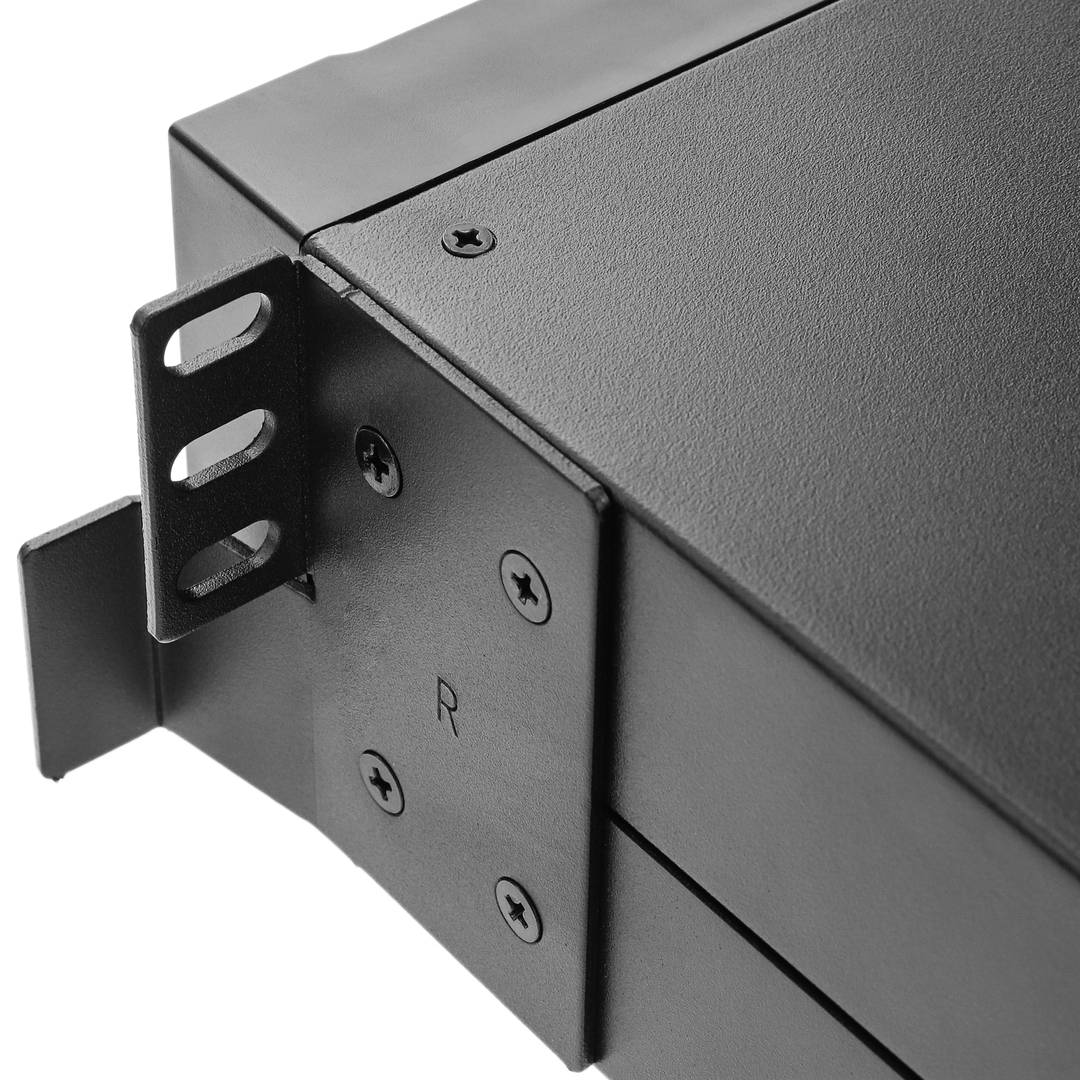
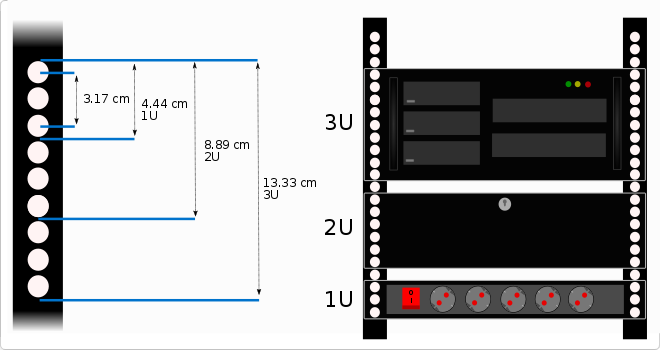
Rack unit (U)
There are several cabinet heights according to the needs of the installation, this height can be measured in rack units (U).
Each rack unit or U is the distance between each horizontal separation to place the different accessories inside the rack. This distance is 1.75 inches that is equal to 4.4445 cm high.
For example, if we say that a rack is 8U we will understand that it has 8 units to install device orAccessories of 4.44 cm in height.
Normally these accessories, like trays, guides, strips, etc. Occupy a unit of U (1U), but we can find that other devices or accessories occupy more units, for example can be a rack box to install a PC, a UPS, etc. It can be said that there is also a half unit of U (0.5U), in this case, two units could be installed in a rack unit.
As far as I knowEndo the units of rack that occupy the devices that we are going to install we will know the height that we need for our rack.
The size of the rack unit (U) is based on the standard specification for racks defined in EIA-310.
![]()
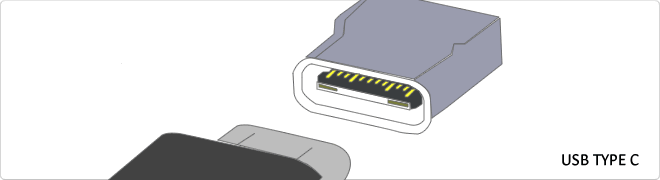
Reversible USB Type-C
USB-C reversible USB version called USB cables USB Type C Type C or USB reversible. The important thing is this type of USB is that it has top and bottom. So you may save the blows that are given involuntarily to connect the connector upside down. It is also characterized in that when connected will make an audible "click". The USB-C or reversible USB cables can reach 10 Gbps and support USB 3.0, 3.1Use is estimated up to 10,000 applications and has some measures 8.4mm x 2.6mm is also compatible with USB 3.1 and USB indicate creators
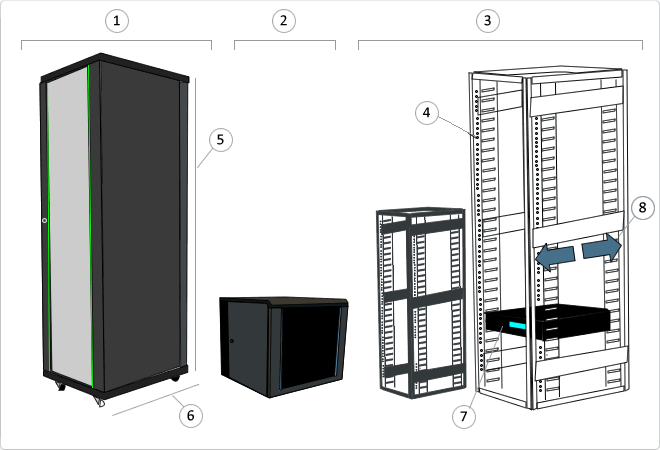
RACK 19
A rack is a metal support designed to house electronic, computer and communications equipment. The measures for the width are normalized to be compatible with most equipment manufacturers. They are also called racks, cabinets, cabinets or closets. Each column has holes at regular intervals called U rack units (Pictured: 4) grouped in threes. The height (Pictured:5) of the racks is standardized and external dimensions of 200 mm by 200 mm. Being normal that from 4U to 46/47U height width types (Pictured: 7). Standard 600 mm or 800 mm Types of background (Pictured: 6) The depth of the frame is not standardized, as this flexibility is granted (Pictured: 8) to the equipment. The most common are: - 450 mm - 600 mm - 800 mm - 900 mm - 1000 mm - 1200 mm Type 19-inch rack can find various types of 19-inch rack. Rack Mural (Pictured: 2): Used to accommodate electronic network. They are the smallest and are anchored to wall. Rack Pie (Pictured: 1): They are used primarily for servers, UPS and network electronics. Open Rack (Pictured: 3): Open Rack Racks are available only modelsstructure, eliminating doors and other accessories.
![]()
Mini USB
The mini USB connectors are smaller than their standard counterparts and have USB fifth pin. The fifth pin is known as the pin ID and is typically not used in mini USB connectors. It was designed to allow later improved USB technology. The mini USB connectors have a cycle life of at least 5000 connections and disconnections, which accommodates the mobile nature of the devices that are designed to interact. The standard USB connectors are generally used with devices that are stationary and not disconnected often.
USB 3.0
USB 3.0 is the second major revision of the standard Universal Serial Bus (USB) connectivity for computing. USB 3.0 has transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbit/s, which is 10 times faster than USB 2.0 (480 Mbit/s). Connector Types 1 - USB type A plug 2 - 3 USB type A female - USB type B 4 - Micro USB B
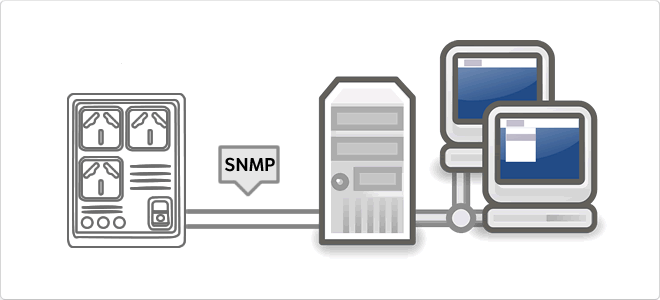
SNMP
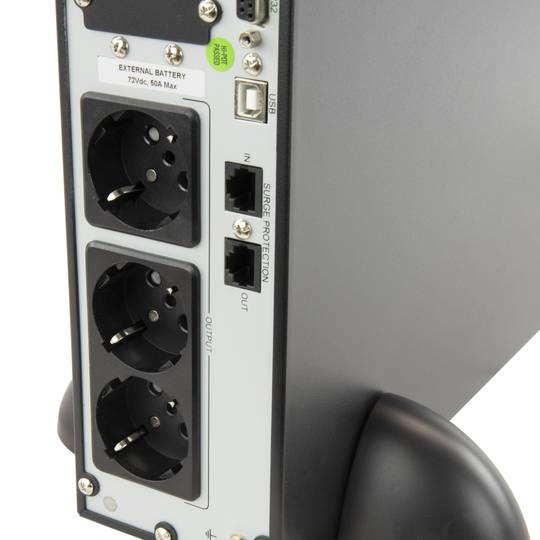
The Simple Network Management Protocol, or SNMP (English Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol for the application layer that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It allows administrators to monitor network performance, find and solve problems, and plan for growth. In an attempt to explain in a simple way, we could imagine that instala card using SNMP to monitor a UPS on a network.
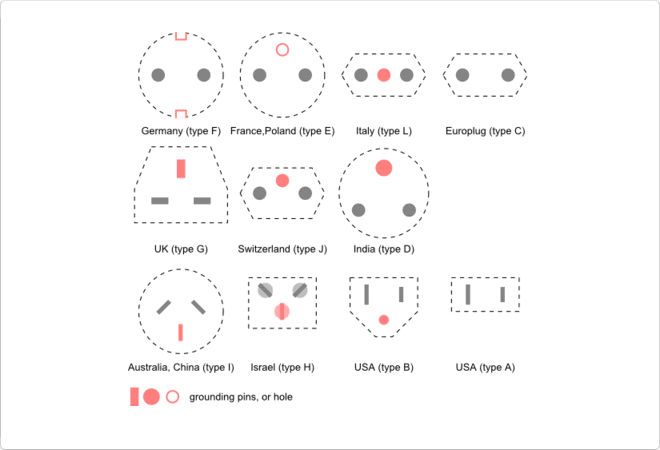
Schuko
In IEC connector or cable with a base (usually plastic) and a plug to connect to the socket (plug), if we put these two things we would get the named SCHUKO is the overall connector. The schuko not determine the type of connector. It would be determined by the specification of the International Electrotechnical Commision (IEC). We leave a small sample of Schukos internationally.
Single-phase
The phase term in domestic premises or homes means you have a single phase alternating current. Usually contracted power in homes is up to 10kW. The difference with the phase installations is that these can be divided into three phases, namely three alternating currents. The single-phase systems can also be divided into parts. Facilities include single-phase 3-wire
RJ45
When we talk about RJ45 ("Registered Jack" 45) we refer to a telecommunications network interface for wired connection of voice and data equipment.
This connector has 8 pins or connections and may have a specific category depending on the data transfer speed and bandwidth (category 5e, 6, etc.)
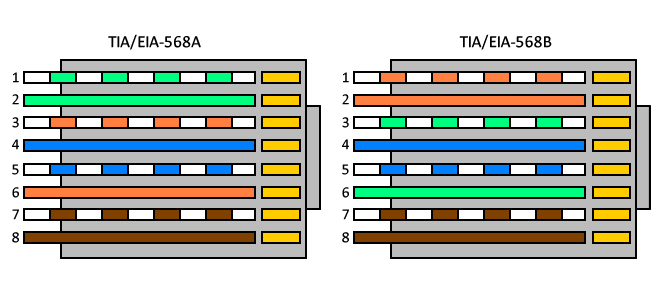
The common application is their use in Ethernet network cables under TIA/EIA-568-B standard that defines the arrangement of pins (pinout), but can also be used for other applications.
- Direct pin diagram:
EIA-568A
Pin No.1: WHITE-GREEN
Pin No.2: GREEN
Pin No.3: WHITE-ORANGE
Pin No.4: BLUE
Pin No.5: WHITE-BLUE
Pin No.6: ORANGE
Pin No.7: WHITE-BROWN
Pin No.8: BROWN
EIA-568B
Pin No.1: WHITE-ORANGE
Pin No.2: ORANGE
Pin No.3: WHITE-GREEN
Pin No.4: BLUE
Pin No.5: WHITE-BLUE
Pin No.6: GREEN
Pin No.7: WHITE-BROWN
Pin No.8: BROWN
- Schematic of crossed pins:
The crossover cable has one end with EIA-568A scheme and the other one with EIA-568B.
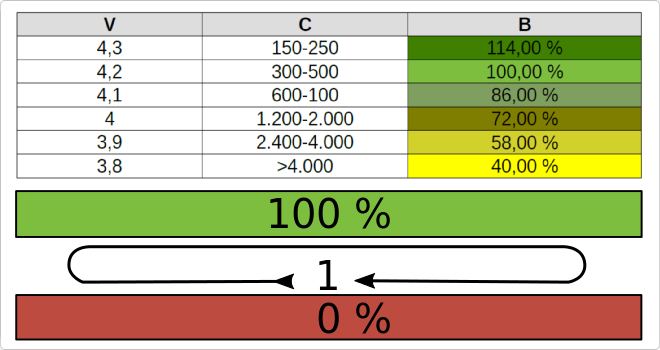
Battery charging cycles
When calculating the life of a battery it will be necessary to know the number of charge cycles that can be performed until the battery does not begin to lose its capacity.
Depending on the type of battery these charging cycles can vary, the most common being the mobile batteries, manufactured Li-Ion or Li-Po, which have a duration of between 300 and 500 charging cycles according to model and manufacturer.
Once thisE limit we will notice how the battery loses duration of operation, arriving to lose up to 25% of its capacity of load.
At this point it will be necessary to evaluate a battery change.
It should be noted that usage and charging habits can significantly affect battery life. For example, factors such as heat, charge the battery several times a day without it is almost exhausted, etc. Will be affectedits duration.
Therefore, to get the most out of the battery we must know when a full charge cycle is performed, and try to avoid misuse of charge, to increase its useful life.
A charging cycle is considered when the battery has been discharged or its 100% charge has been used.
The manufacturers advise that the charge is never made below the 58% battery, since the battery voltage would not fall so lowTo, so you could end up winning up to 4000 charge cycles.
Tips to increase the life of a battery.
- Avoid extreme heat or cold or very long applications of the device.
- Charge the battery as often as you can.
- Fully discharge the battery from time to time.
- Do not let the battery run out completely before charging.
Below is a table with theDifferent voltages (V), charge cycles (C) and battery percentage (B).
![]()
![play_button]() Watch video
Watch video