Impedance
The impedance (Z) is a measure of opposition that a circuit to a current when a voltage is applied. The impedance extends the concept of resistance circuits alternating current (AC), and has both magnitude and phase, unlike resistance, which has only magnitude. When a circuit is powered with direct current (DC), there is no distinction between the impedance and resistance; the latter can be thought csa impedance with zero phase angle.
Hz
One hertz is one cycle per second, meaning repeating cycle as an event. For example, hertz is applied physics measuring the number of times for a second wave (either acoustic or electromagnetic) is repeated or can be applied, among other uses, to ocean waves that reach the Beach vibrations per second or a solid. The quantity that measures the frequency hertz is called,in this regard, the inverse of the period. One hertz is an oscillation frequency of suffering a particle over a period of one second.
GSM
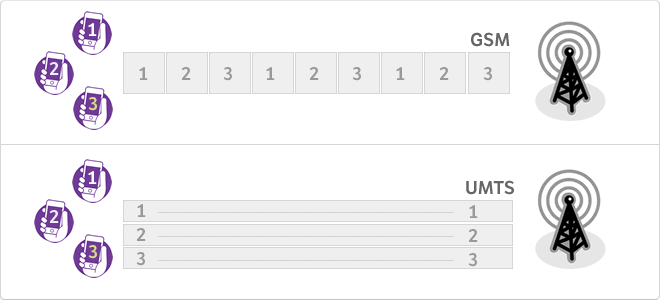
The global system for mobile communications (English Global System for Mobile communications, GSM, and originally from the French groupe spécial mobile) is a standard system, royalty-free, digital mobile phone. A GSM client can connect through your phone to your computer and send and receive emails, faxes, surf the Internet, access to the computer network security acompany (LAN/Intranet) and use other functions of digital data, including short message service (SMS) or text messages. What are the differences between GSM and UMTS? The GSM system operates by TDMA, ie, time is divided into slots and each user is assigned a slot, ie, a period for which data can be transmitted. Therefore each channel is shared by a ndetermined number of users. The system is a UMTS (WCDMA) code division multiple access broadband. In this system there are no time slots and GPRS. All users transmit simultaneously on the channel, but each user signals are encoded with a unique code so that even though we think that an "indecipherable signal" is formed by using the same frequencies simultaneously, It is not toyes, because the base station is capable of decoding and re perfectly separate each of the communications received from different users. This obviously implies a much higher channel utilization, to not share in time.
![]()
dBi
The dBi isotropic or decibel is a unit for measuring the gain of an antenna in reference to a theoretical isotropic antenna. The value dBi corresponds to the gain of an ideal antenna (theoretical) radiating the received power of a device to which it is connected, and which also transmits the signals received from space without regard either external or additional gains or losses powers.
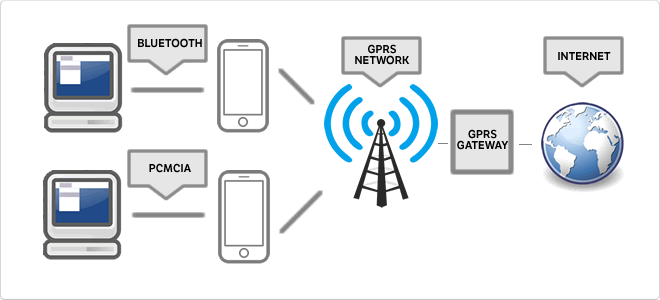
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) or general packet radio service created in the 80s is an extension of the Global System for Mobile Communications (Global System for Mobile Communications or GSM) for the transmission of data by packet switching. A similar service for mobile phones, the IS-136 system. It allows transfer rates of 56-114 kbps. These Class A devicesThey can simultaneously use GPRS and GSM services. Only Class B may be connected to one of the two services at all times. While GSM service (voice or SMS) is used, the GPRS service, which automatically restarts when the GSM service ends is suspended. Most mobile phones are of this type. Class C are alternately connected to one or another service. Switching between GSM and GPRS shouldperformed manually.
UMTS
Universal mobile telecommunications system (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System or UMTS) is one of the technologies used by mobile third-generation successor to GSM, because the GSM technology itself could not follow an evolutionary path to get to providing services considered third generation. Although initially is designed for use in mobile phones, the UMTS network is not LIMITADaa these devices and it can be used by others. What are the differences between GSM and UMTS? The GSM system operates by TDMA, ie, time is divided into slots and each user is assigned a slot, ie, a period for which data can be transmitted. Therefore each channel is shared by a number of users. The system is a UMTS (WCDMA) code division multiple access dand broadband. In this system there are no time slots and GPRS. All users transmit simultaneously on the channel, but each user signals are encoded with a unique code so that even though we think that an "indecipherable signal" is formed by using the same frequencies simultaneously, It is not, because the base station is capable of decoding and re perfectly separate each of the communicationsreceived from different users. This obviously implies a much higher channel utilization, to not share in time.
![]()
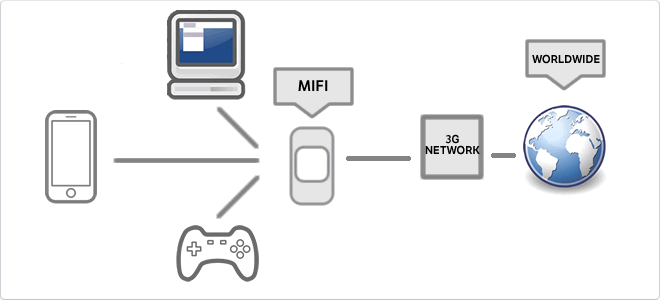
MiFi
MiFi is a mobile router that acts as an access point to the Internet via 3G or later. You can connect to one or more devices at once by WiFi. It can be used with multiple WiFi devices such as desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.
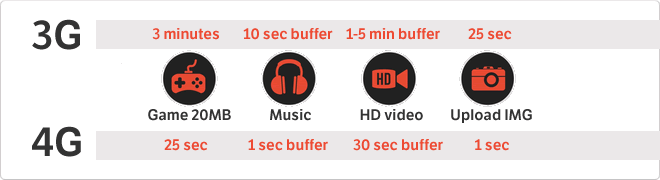
4G
4G is the next generation of technology that the International Telecommunication Union has created for transferring data via the Internet. The speed is 100 MB/s downstream and 50 MB/s upstream, with a bandwidth of 20 MHz. The idea that used to wield the great value of 4G format that society is consuming more video and heavy images and this will make the mobile phone supports it. A continuación show you a small graphic comparison between 3G and 4G in the most common uses computer-related.
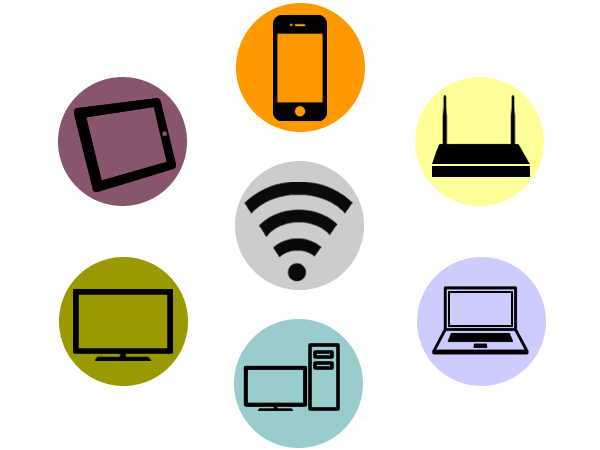
Wifi
The Wifi technology is a wireless communication mechanism between devices. This technology allows you to connect devices such as computers, laptops, mobile etc... to the Internet or communicate with the devices themselves.
Applications can be several, among the most common are the access points, ideal for giving and sharing a connection signal to multiple devices. It is the typical configuration of a home user.
Repeater, ideal to repeat and amplify weak signal.
The power and range between devices basically depends on the antenna and its hardware.
The wireless signals work under a unified standard regulations, the standard that is based on the IEEE 802.11. These include IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11n working at 11 Mbit/s, 54 Mbit/s and 300 Mbit/s, respectively.
Being any device with a standardized protocol such technology can connect to another using the same technology, making it a kind of universal connection.
The wireless networks are characterized by the ease and convenience of making connections in infrastructure, since it is not necessary to perform network cable installations.
it also allows connecting a lot of devices to a single node.
![]()
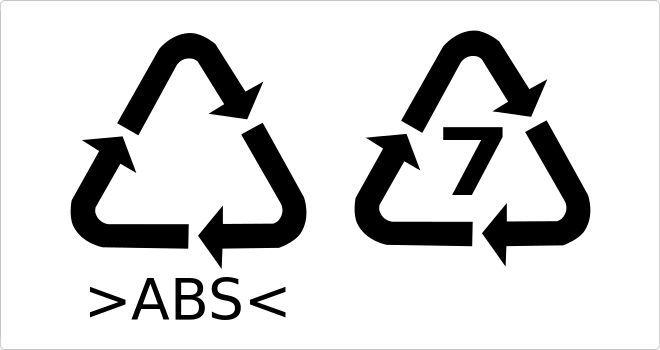
ABS
ABS material (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is a type of thermoplastic that is very resistant to impact or shock.
Its applications are several, for example is a material widely used in the manufacture of interiors or components of cars such as moldings, as well as in products for domestic use such as toys, tools, housings of electrical devices etc.
One of its most important characteristics is its great tenacidad in almost all types of temperatures.
Being a very hard material has good chemical resistance, low water absorption and high resistance to abrasion, where other types of plastics would be more brittle.
This type of material is becoming very famous in the particular field and widely used due to the great growth in the sales of domestic 3D printers, the main printing raw material.next to the PLA.
Identification of ABS
Parts that are made of ABS material must be marked in accordance with ISO 11469 (DIN 58840).