04/18/2024 10:39 p.m.
https://cablematic.com/en/products/inductive-proximity-sensor-high-frequency-sn-4mm-6-36-vdc-pnp-no-m12-TZ013/
https://cablematic.com/en/products/inductive-proximity-sensor-high-frequency-sn-4mm-6-36-vdc-pnp-no-m12-TZ013/
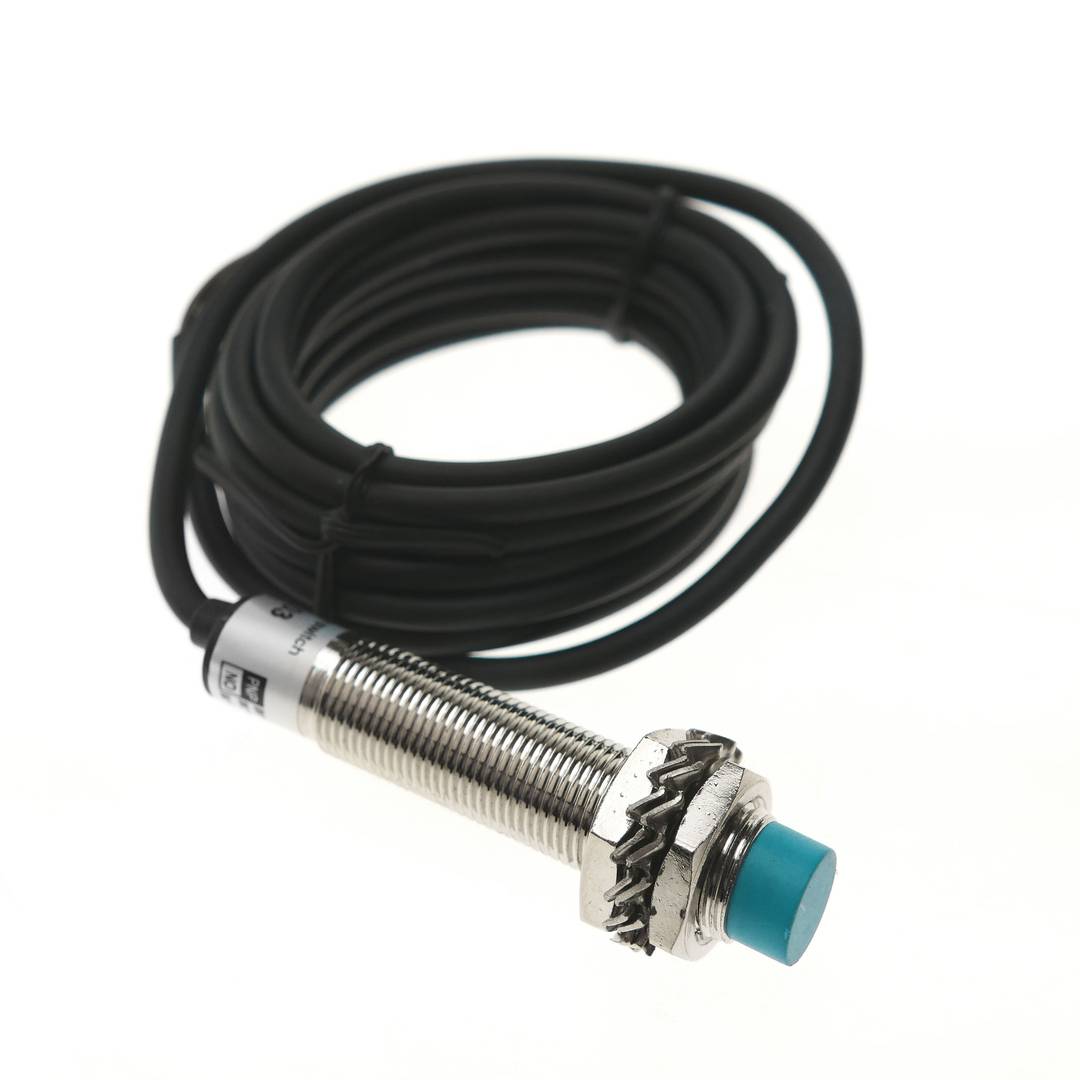
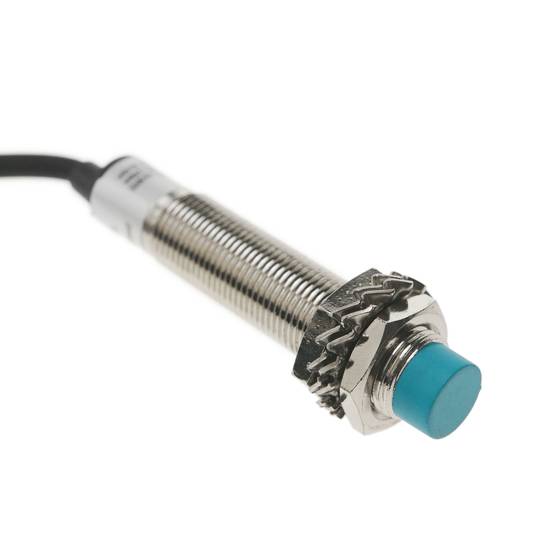
Inductive proximity sensor high frequency Sn: 4mm 6-36 VDC PNP NO M12
REF: TZ013
Specifications
- High frequency inductive proximity sensor. Inductive proximity switch.
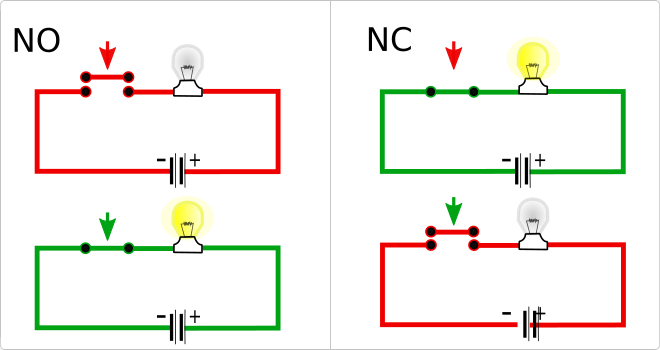
- Output type PNP (positive + output) and NO (normally open).
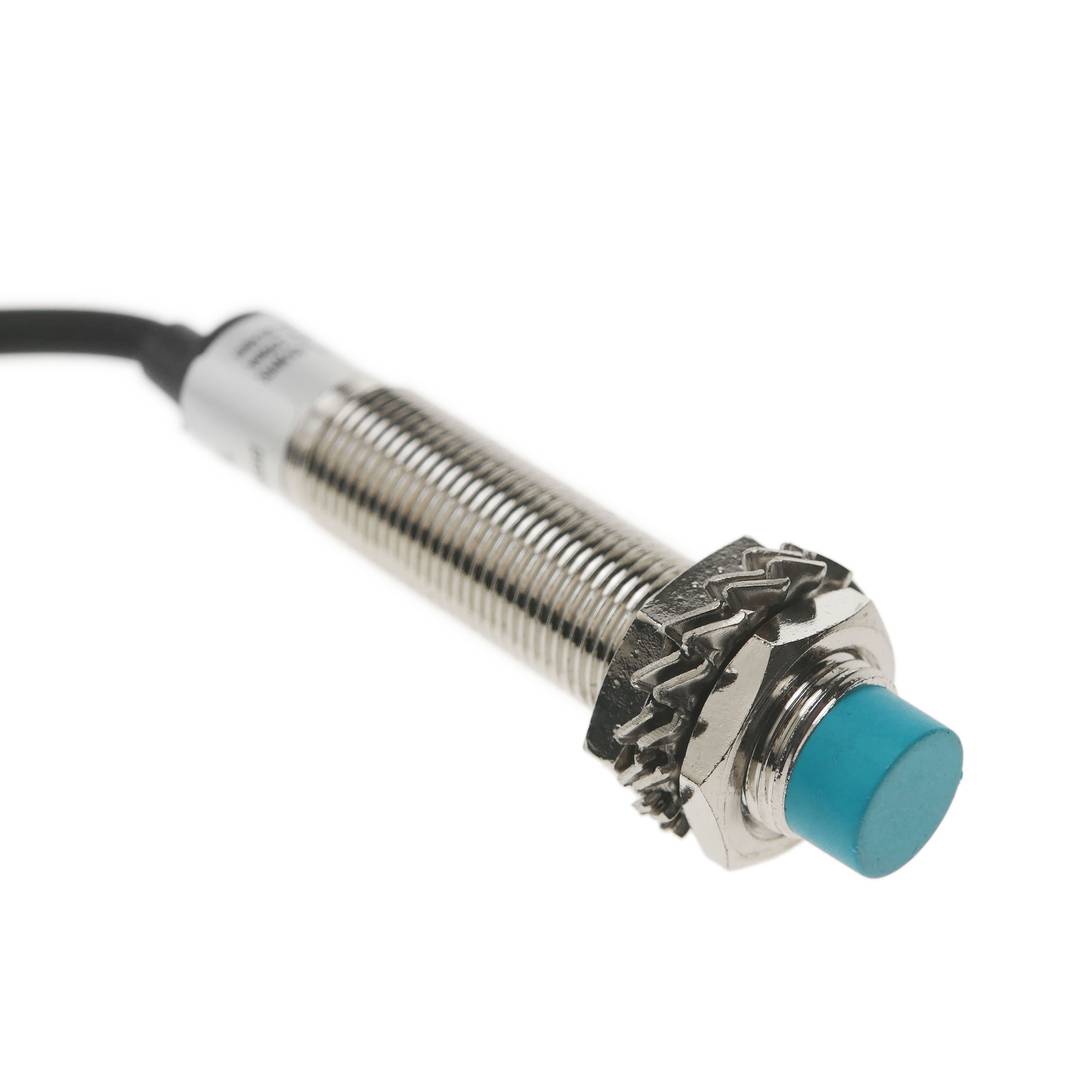
- Round type sensor with diameter 12 mm (M12), and length 65 mm.
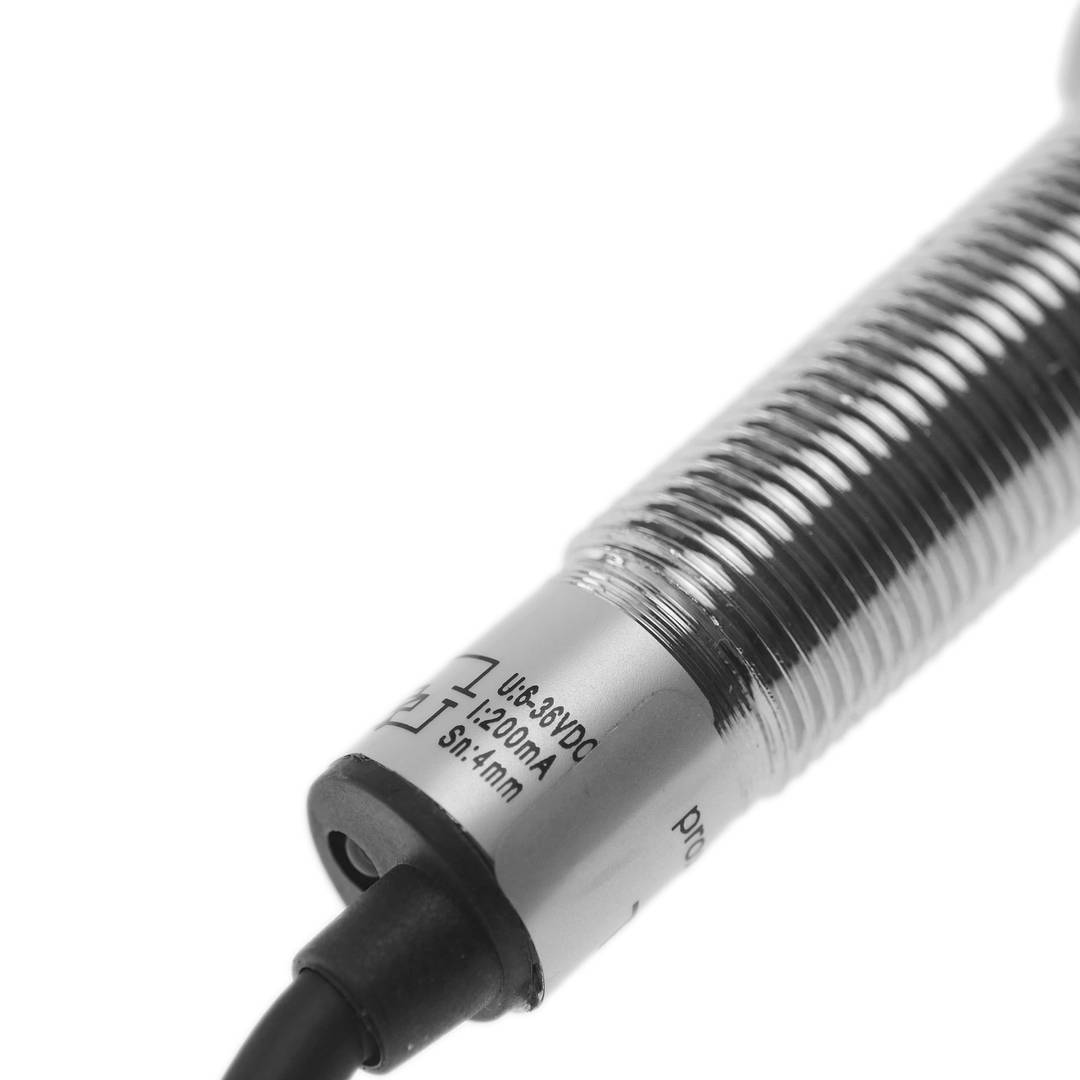
- Operating voltage: 6-36 VDC (200 mA).
- Sensing distance (Sn): 4 mm.
PVP
€19.24
Price including VAT:
€19.24
PVD
€16.30
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
Buy before:
Receive it:
Thursday 25
Delivery times are approximate. Cablematic is not responsible for delays.
warranty
returns
safe
Specifications
- High frequency inductive proximity sensor. Inductive proximity switch.
- Output type PNP (positive + output) and NO (normally open).
- Round type sensor with diameter 12 mm (M12), and length 65 mm.
- Operating voltage: 6-36 VDC (200 mA).
- Sensing distance (Sn): 4 mm.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
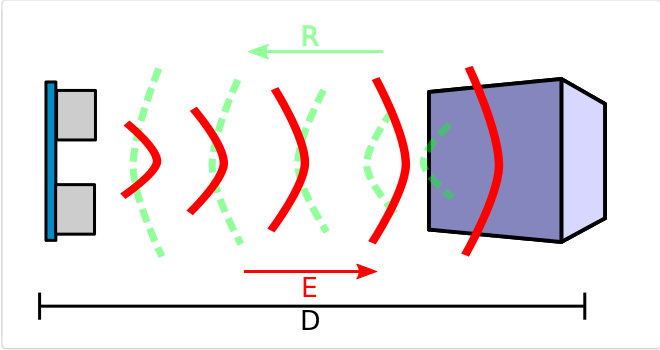
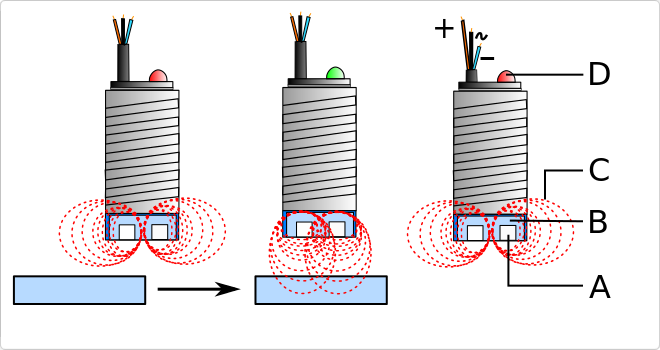
High frequency proximity sensor. Transducer that detects objects or signals that are near the sensing element. Inductive proximity sensor designed to work by generating a magnetic field and detecting the current losses of said field generated when ferrous and non-ferrous detection objects are introduced into it.
Specifications
Specifications
- High frequency inductive proximity sensor. Inductive proximity switch.
- Output type PNP (positive + output) and NO (normally open).
- Round type sensor with diameter 12 mm (M12), and length 65 mm.
- Operating voltage: 6-36 VDC (200 mA).
- Sensing distance (Sn): 4 mm.
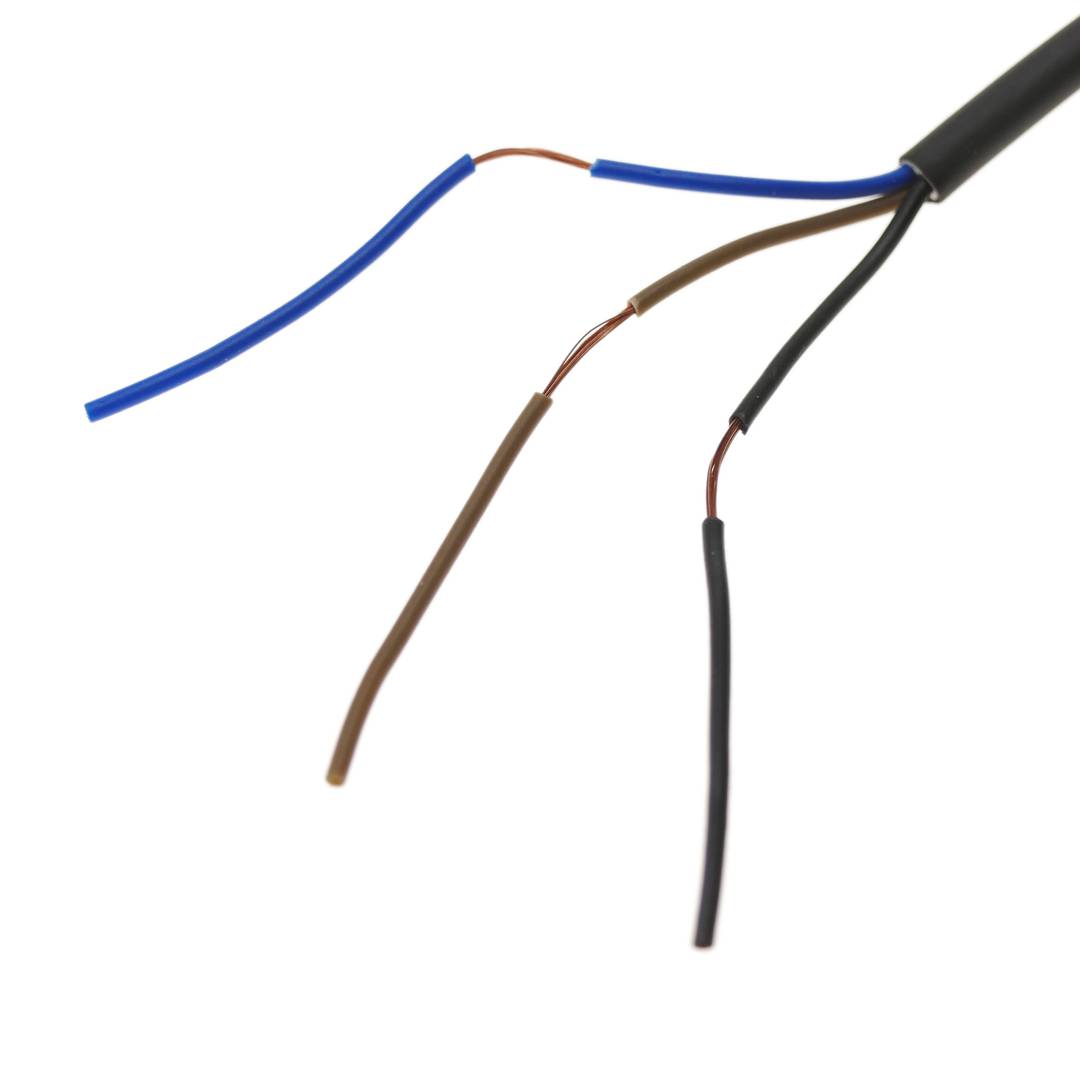
- It has a cable terminated in 3 wires (black, blue and brown).
- Gross Weight: 100 g
- Number of packages: 1
- Packages size: 11.0 x 8.2 x 5.6 cm
Technical terms
- VDC
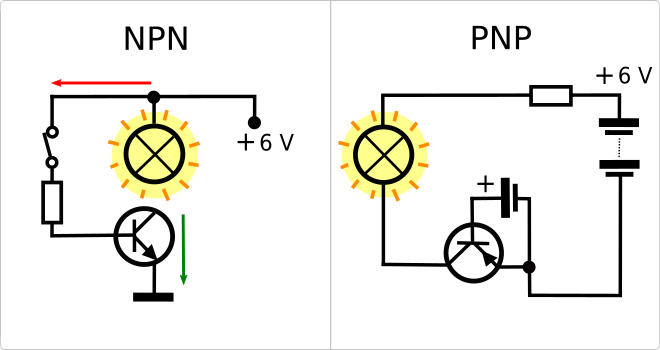
- Differences between PNP and NPN
- Differences between NO and NC
- Types of proximity sensors
- Inductive Proximity Sounds
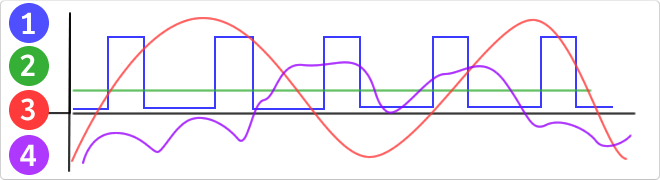
VDC
VDC would be the abbreviation for Volt Direct Current which translated would volts direct current. The idea of ??this type is unidirectional current to the load. Direct current is normally produced by batteries, thermocouples, solar cells and a dynamo electric machine type. The direct current can flow in conductors such as wires, but may also flow through semiconductors, insulators ... In the image: 1 - current per pulse 2 - Direct Current (DC) 3 - Alternating Current (AC) 4 - Variable Current