04/28/2024 1:05 a.m.
https://cablematic.com/en/products/wireless-schuko-plug-z-wave-3500w-230vac-white-WZ002/
https://cablematic.com/en/products/wireless-schuko-plug-z-wave-3500w-230vac-white-WZ002/
PVP
€39.67
€11.11
Price including VAT:
€11.11
PVD
€33.97
€9.51
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
returns
OUTLET
We will notify you when it is back in stock.
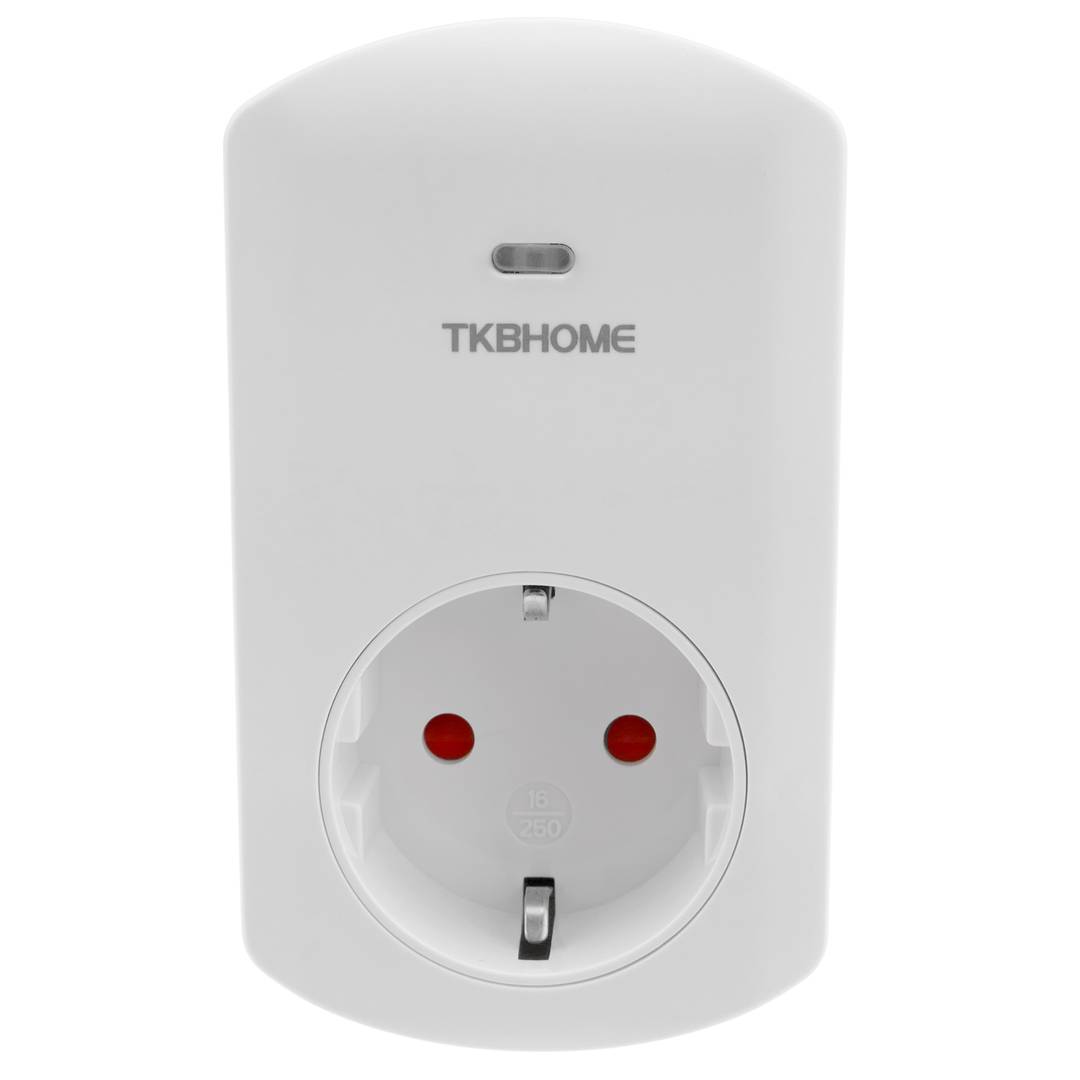
Specifications
- Z-Wave plug.
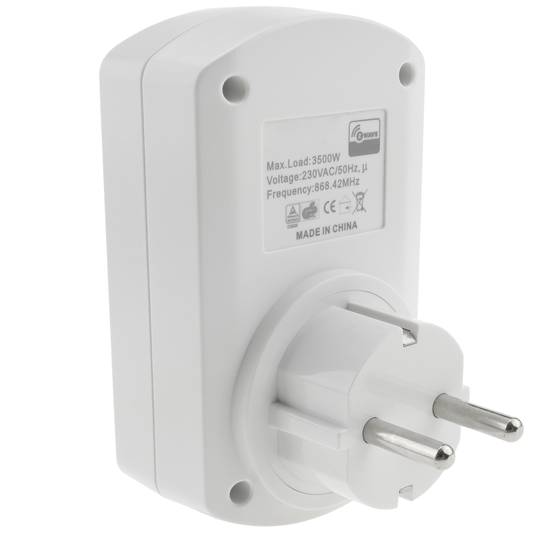
- Maximum power: 3500W.
- Voltage: 230VAC/50Hz.
- Operating range of 30m distance between the nearest Z-Wave device.
- Schuko type plug.
More info
Plug based on Z-Wave wireless technology. The Z-Wave protocol allows radio-frequency wireless communication. Protocol designed for control, monitoring and home automation. Z-Wave is compatible with devices from different manufacturers that use the same protocol.
Wireless plug specifications
Wireless plug specifications
- Z-Wave plug.
- Maximum power: 3500W.
- Voltage: 230VAC/50Hz.
- Operating range of 30m distance between the nearest Z-Wave device.
- Schuko type plug.
- Size: 102 x 82 x 68 mm.
- Low consumption RF communication.
- Wireless network type mesh all the same, without the need for coordination nodes.
- Operating in the sub-1GHz band. It has no interference with other technologies in the range2.4 GHz (bluetooth, ZibBee, etc.).
- Operating frequency: 868.42 MHz.
- Designed to be controlled from mobile devices (tablets, mobile phones, etc.).
- Data transmission up to 100 Kbps with AES125 encryption, IPV6, and multi-channel operation.
- MAC and PHY specifications (ITU-T G.9959 regulation).
- Compatible between different versions of Z-Wave.
- Gross Weight: 170 g
- Number of packages: 1
Technical terms
- Hz
- Schuko
- Z-wave
- RF or Radio Frequency
- Bluetooth
Hz
One hertz is one cycle per second, meaning repeating cycle as an event. For example, hertz is applied physics measuring the number of times for a second wave (either acoustic or electromagnetic) is repeated or can be applied, among other uses, to ocean waves that reach the Beach vibrations per second or a solid. The quantity that measures the frequency hertz is called,in this regard, the inverse of the period. One hertz is an oscillation frequency of suffering a particle over a period of one second.